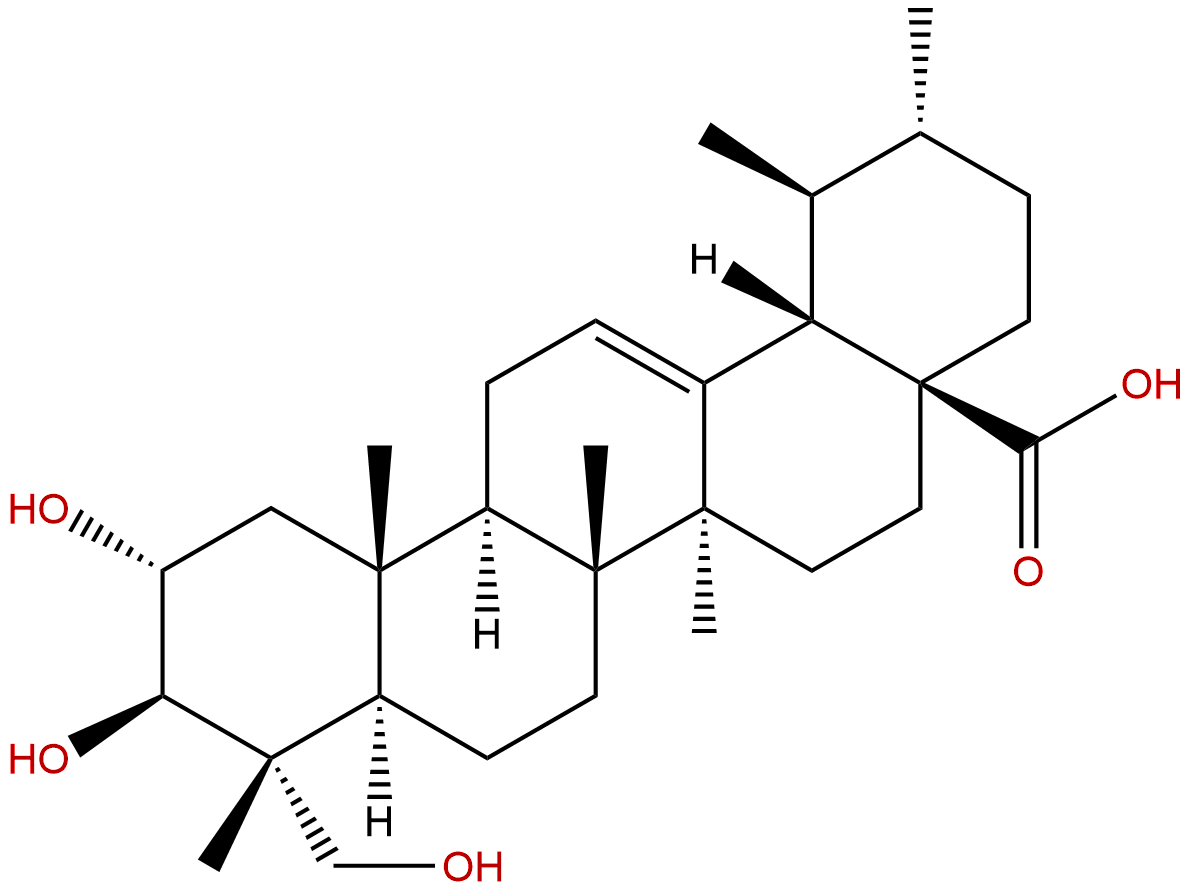
Asiatic acidCAS No.:464-92-6 |
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0203 |
| Formula: | C30H48O5 |
| Mol Weight: | 488.709 |
| Botanical Source: | Centella asiatica (L.)Urb. |
Product name: Asiatic acid
Synonym name: Dammarolic acid
Catalogue No.: BP0203
Cas No.: 464-92-6
Formula: C30H48O5
Mol Weight: 488.709
Botanical Source: Dipterocarpus pilosus, Dryobalanops aromatica and others
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Asiatic acid is a pentacyclic triterpene contained in medicinal plants, can be used as an agent for increasing sensitivity of colon cancer cells to treatment with CPT-11 or as an agent for reducing adverse effects of CPT-11.[1]
Asiatic acid has been reported to induce apoptosis of various human cancer cells, it may exert anti-tumorigenesis through inhibitory actions in NO and COX-2 signals.[2]
Asiatic acid ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine experimental colitis via suppressing mitochondria-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation, its potential usage in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.[3]
Asiatic acid shows antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic activity in diabetic rats.[4]
Asiatic acid (AA) has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, it inhibits LPS-induced ALI in mice by inhibiting inflammatory cytokine production, which is mediated via blocking of the TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway.[5]
Asiatic acid can inhibit cell proliferation through regulating the expression of focal adhesion kinase in multiple myeloma cells.[6]
References:
[1] Bunpo P, Kataoka K, Arimochi H, et al. J Med Invest, 2005, 52(1-2):65-73.
[2]Park B C, Paek S H, Lee Y S, et al. Biol Pharm Bul, 2007, 30(1):176-9.
[3] Guo W, Liu W, Jin B, et al. Int Immunopharmacol, 2015, 24(2):232-8.
[4] Ramachandran V, Saravanan R, Senthilraja P. Phytomed IntJ Phytothery Phytopharmacol, 2014, 21(3):225-32.
[5] Zhiling Li, Xianzhong Xiao, Mingshi Yang. Inflammation, 2016:1-7.
[6] Zhang J, Ai L, Lv T, et al. Oncol Lett, 2013, 6(6):1762-6.
[7] Tiwari R K, Chanda S, Deepak M, et al. J Chem Pharm Res, 2010(3):223-9.
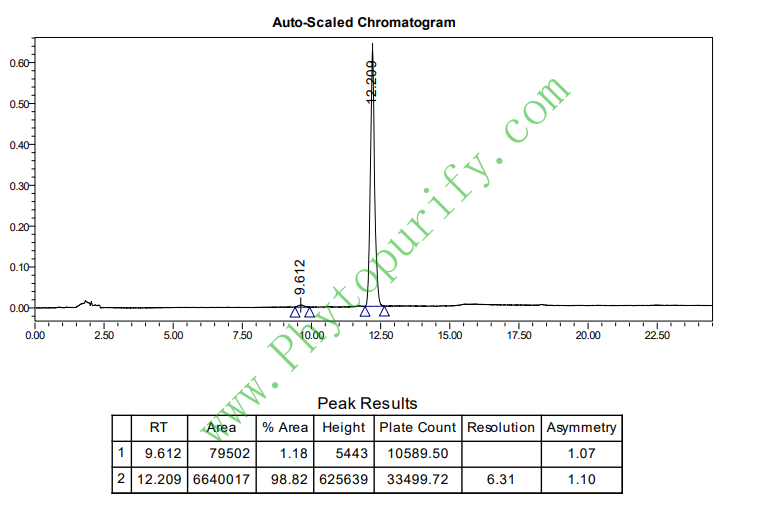
HPLC of Asiatic acid