
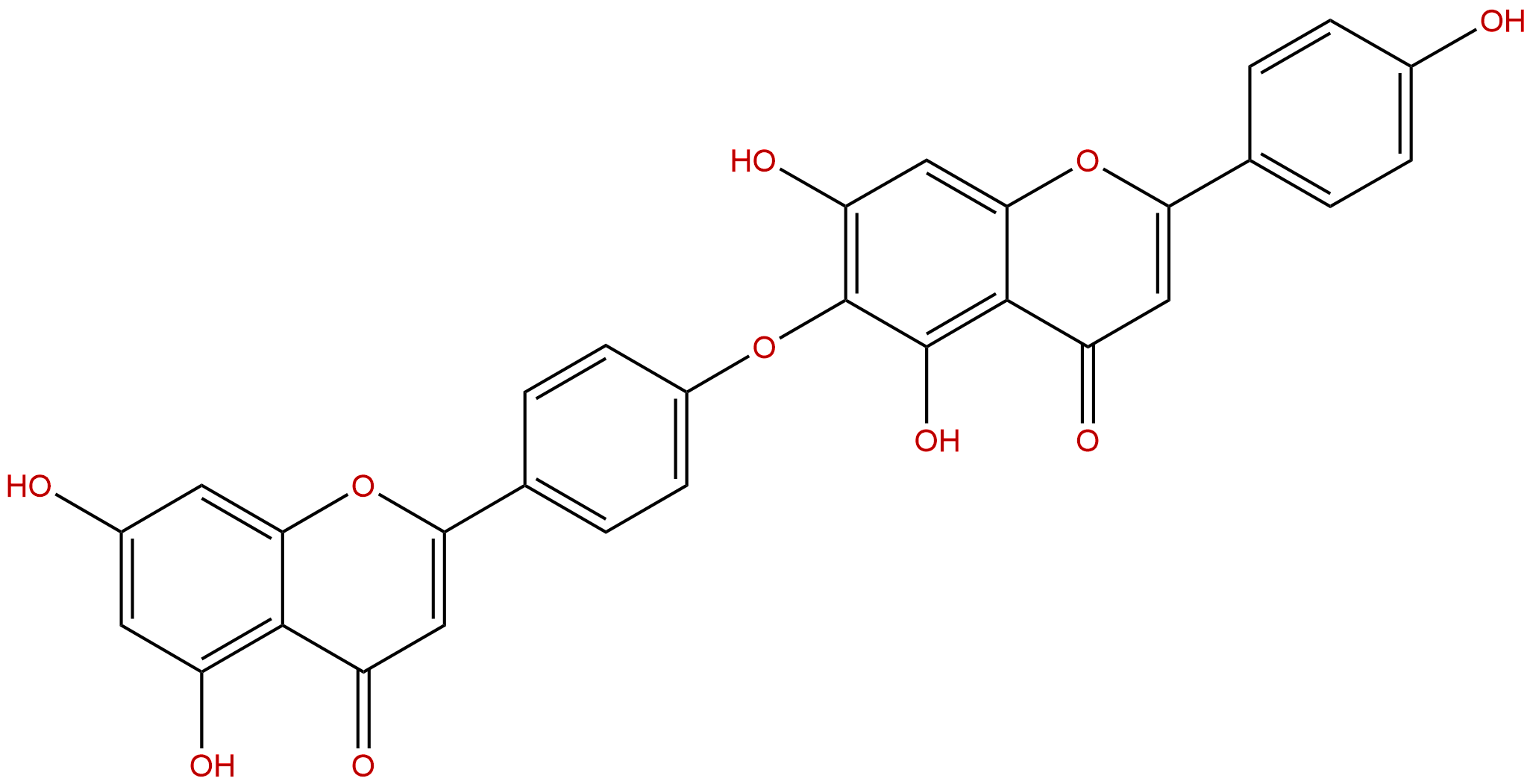
HinokiflavoneCAS No.:19202-36-9 |
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0729 |
| Formula: | C30H18O10 |
| Mol Weight: | 538.464 |
| Botanical Source: | Selaginellae herba |
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP0729
Cas No.: 19202-36-9
Formula: C30H18O10
Mol Weight: 538.464
Botanical Source: Obt. from leaves of Chamaecyparis obtusa. Also from Psilotum triquetrum. Present in the Cupressaceae, Cycadales and many other plants
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Hinokiflavone has significant cytotoxicity, it has inhibition of MMP-9.
References:
Planta Med. 1989 Apr;55(2):166-8.
Hinokiflavone, a cytotoxic principle from Rhus succedanea and the cytotoxicity of the related biflavonoids.
Hinokiflavone (1) was isolated as the cytotoxic principle from the drupes of Rhus succedanea L.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A comparison of the cytotoxicity of 1 and other related biflavonoids, including amentoflavone (2), robustaflavone (3), agathisflavone (4), rhusflavone (5), rhusflavanone (6) and its hexaacetate (7), succedaneaflavanone (8) and its hexaacetate (9), cupressuflavone (10), neorhusflavanone (11), volkensiflavone (12) and its hexamethyl ether (13), spicataside (14) and its nonaacetate (15), morelloflavone (16) and its heptaacetate (17) and heptamethyl ether (18), GB-1a (19) and its hexamethyl ether (20) and 7"-O-beta-glucoside (21), and GB-2a (22), indicates that an ether linkage between two units of apigenin as seen in 1 is structurally required for significant cytotoxicity. Compounds 13 and 20 also demonstrated significant cytotoxicity.