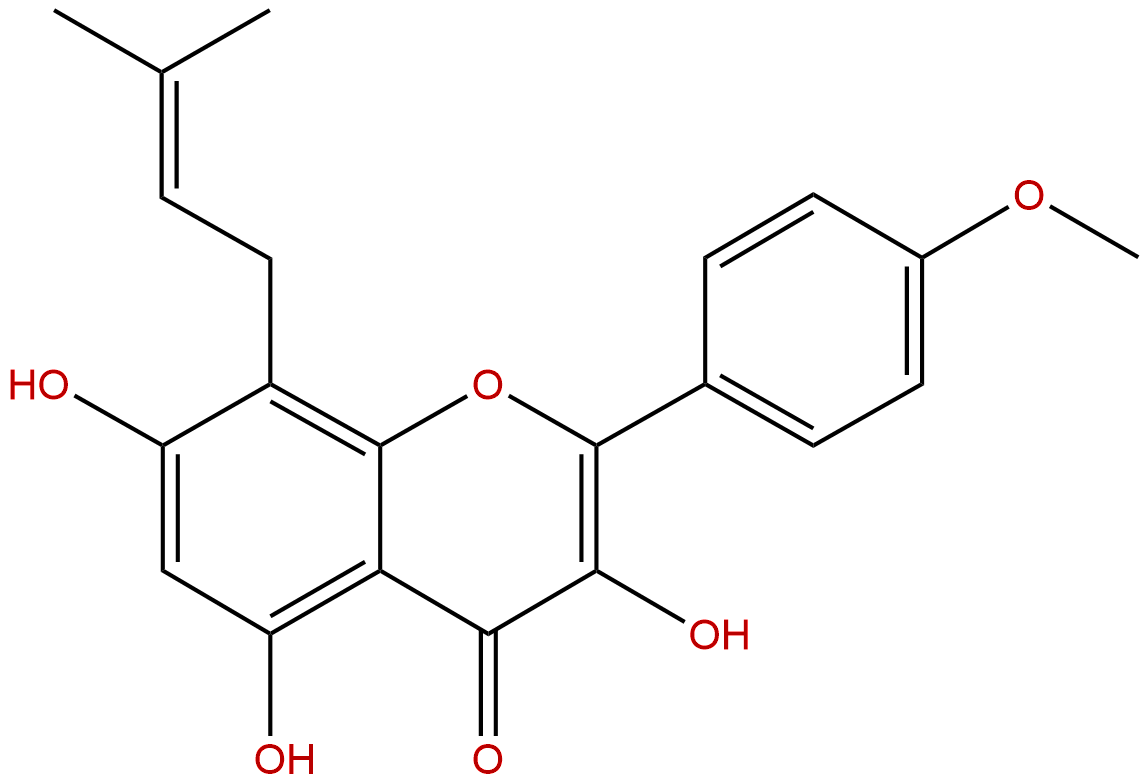
IcaritinCAS No.:118525-40-9 |
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0759 |
| Formula: | C21H20O6 |
| Mol Weight: | 368.385 |
| Botanical Source: | Epimedii folium |
Synonym name: Anhydroicaritin
Catalogue No.: BP0759
Cas No.: 118525-40-9
Formula: C21H20O6
Mol Weight: 368.385
Botanical Source: Epimedium spp.
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Icaritin, a potent inhibitor of transcription factor SREBPs, which exhibits a variety of biological activities, such as activation of cancer cell apoptosis and inhibition of growth, hormone regulation, protection against beta amyloid-induced neurotoxicity, and promotion of neuronal and cardiac cellular differentiation. Icaritin shows potent anti-leukemia activity on chronic myeloid leukemia in vitro and in vivo by regulating MAPK/ERK/JNK and JAK2/STAT3 /AKT signalings.
References:
Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 30;6(12):10460-72.
Icaritin suppresses multiple myeloma, by inhibiting IL-6/JAK2/STAT3.
Icaritin is an active prenylflavonoid derived from Epimedium genus, a traditional Chinese medicine. Icaritin has a wide range of pharmacological and biological activities, including cardiovascular function improvement, hormone regulation and antitumor activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we investigated the effect of Icaritin on multiple myeloma (MM) in vitro and in vivo. Icaritin inhibited cell growth of MM cell line and primary MM cells. In contrast, Icaritin had low or no cytotoxic effect on normal hematopoiesis. We also demonstrated that in MM xenograft mouse models, Icaritin suppressed tumor growth and decreased serum IL-6 and IgE levels, but did not show adverse reactions such as body weight loss. The anti-MM activity of Icaritin was mainly mediated by inhibiting IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling.
CONCLUSIONS:
We suggest that Icaritin can be further tested in clinical trials in MM.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Nov 19;504(3):147-53.
Proliferation-stimulating effects of icaritin and desmethylicaritin in MCF-7 cells.
Icariin, Icaritin and desmethylIcaritin are constituents of Epimedium with a similar structure to genistein and daidzein.
CONCLUSIONS:
Using the modified MCF-7 cell proliferation assay (E-SCREEN assessment system), these compounds were tested for their estrogen-like activities. Icaritin and desmethylIcaritin, but not icariin, strongly stimulated the proliferation of MCF-7/BUS cells. Cell cycle analysis revealed that the proliferation stimulatory effect was associated with a marked increase in the number of MCF-7/BUS cells in S phase and a significant increase in the G2/M population, with effects similar to those of estradiol. These actions were dose dependent (range from 1 nM to 10 microM) and could be significantly inhibited by the specific estrogen receptor antagonist ICI 182,780 [7 alpha-[9(4,4,5,5,5-pentafluoropentyl)sulfinyl]nonyl)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17beta-diol)]. The estrogen receptor-regulated progesterone receptor and PS2 mRNA levels were increased by treatment with Icaritin or desmethylIcaritin within 24 h and the effects were also reversed by ICI 182,780.
CONCLUSIONS:
It was concluded that Icaritin and desmethylIcaritin are novel phytoestrogens and that the estrogenic effects of Icaritin and desmethylIcaritin are mediated by the estrogen receptor.
Phytomedicine. 2014 Oct 15;21(12):1633-7.
Synergistic inhibitory effect of Icariside II with Icaritin from Herba Epimedii on pre-osteoclastic RAW264.7 cell growth.
Increasing evidence shows the therapeutic superiority of herbal extracts in comparison to isolated single constituents. One of the reasons may be attributed to the synergy effect of compound combinations. Flavonoids from Herba Epimedii have been shown to have therapeutic effect against bone loss. Our previous study showed that Icariside II inhibited pre-osteoclast RAW264.7 growth. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the activity of Icariside II is synergized by other components of Herba Epimedii.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The inhibitory activity of Icariside II was significantly enhanced in the presence of the extract of Herba Epimedii (EHE) at the ratio of 1:1, 1:5 and 1:10. Icaritin, another flavonoid constituent, was shown here to inhibit RAW264.7 growth in a dose-dependent manner. Further, we found that Icariside II, together with Icaritin, synergistically inhibited RAW264.7 growth. The synergistic effect is significant when the ratio of Icariside II and Icaritin was 10:1, 5:1, 1:1, 1:2, and 1:5, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, Icaritin were an active component. The inhibitory activity of Icariside II on pre-osteoclast RAW264.7 growth was synergized by Icaritin, which maybe contribute to the efficiency of Herba Epimedii extract on curing bone-related diseases, such as osteoporosis.
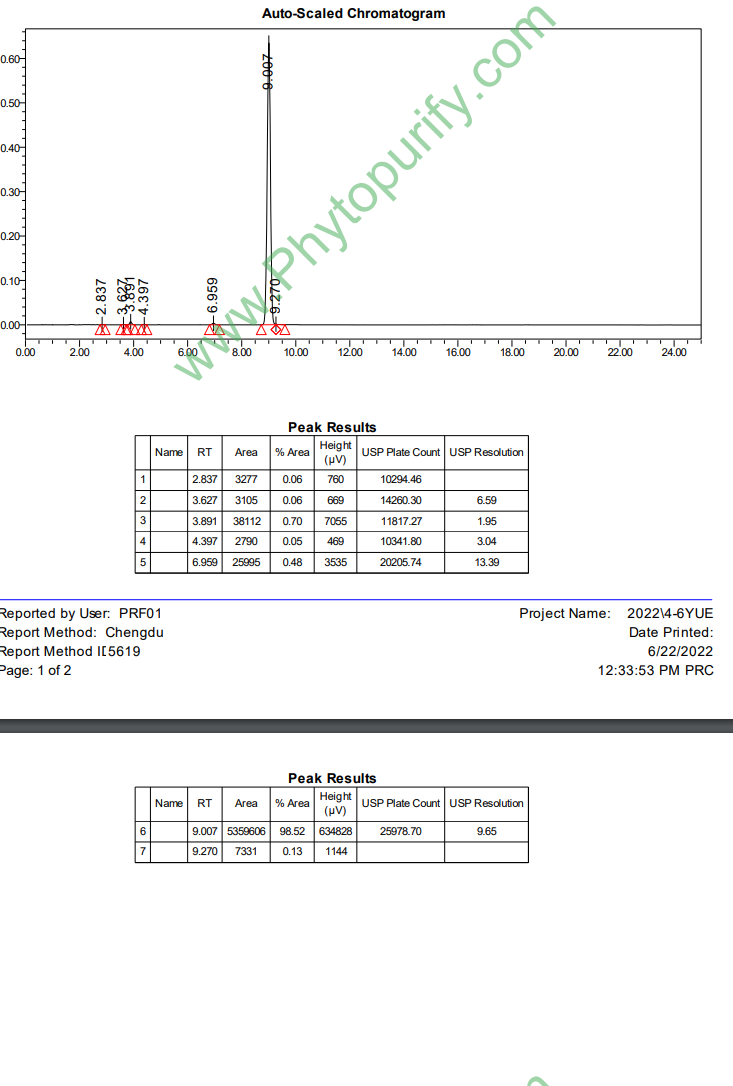
HPLC of Icaritin