
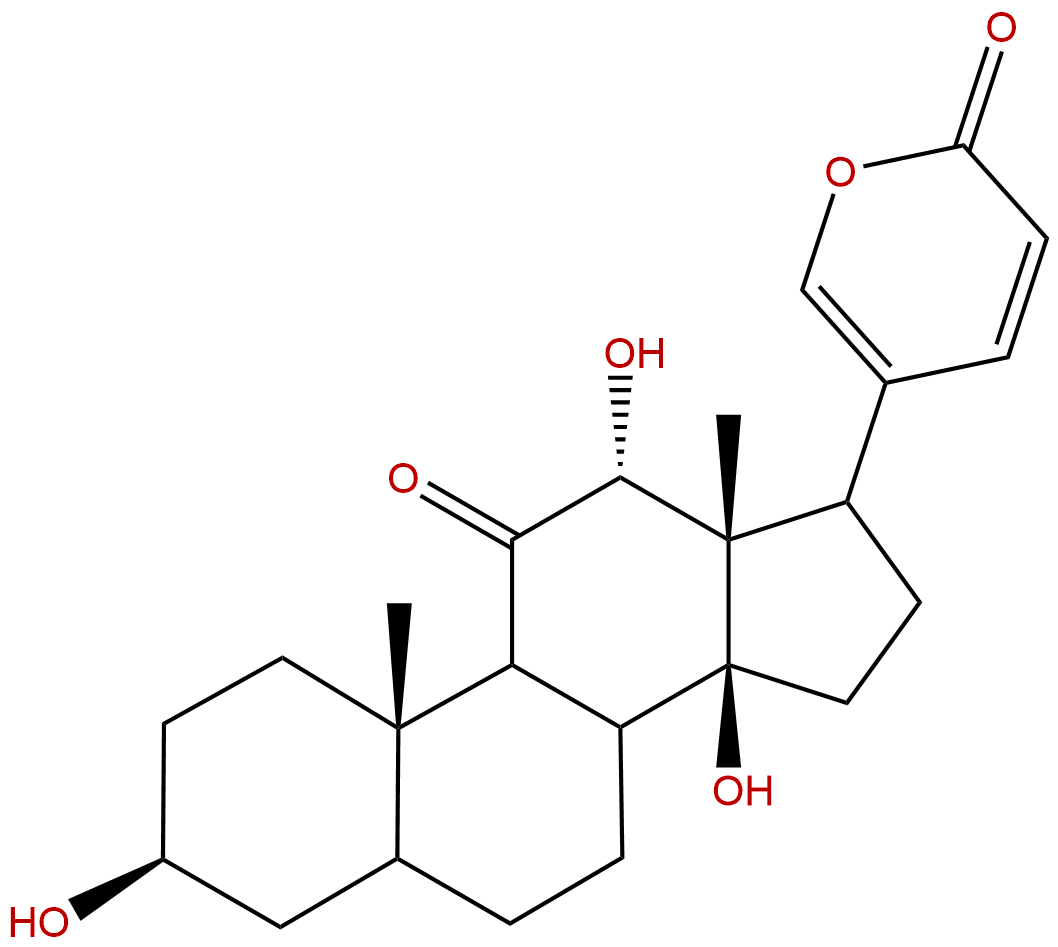
PseudobufarenoginCAS No.:17008-69-4 |
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP3331 |
| Formula: | C24H32O6 |
| Mol Weight: | 416.514 |
| Botanical Source: | Bufonis Venenum |
Product name: Pseudobufarenogin
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP3331
Cas No.: 17008-69-4
Formula: C24H32O6
Mol Weight: 416.514
Botanical Source:
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Steroids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
We provide solution to improve the water-solubility of compounds, thereby facilitating the variety of activity tests and clinic uses.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Pseudobufarenogin(ψ-bufarenogin), a novel anti-tumor compound, suppresses liver cancer growth by inhibiting receptor tyrosine kinase-mediated signaling. ψ-Bufarenogin shows inhibition of human kidney Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase activity.
References:
Toxicon. 2016 Feb;110:27-34.
Bufadienolides from parotoid gland secretions of Cuban toad Peltophryne fustiger (Bufonidae): Inhibition of human kidney Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase activity.
Parotoid gland secretions of toad species are a vast reservoir of bioactive molecules with a wide range of biological properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Herein, for the first time, it is described the isolation by preparative reversed-phase HPLC and the structure elucidation by NMR spectroscopy and/or mass spectrometry of nine major bufadienolides from parotoid gland secretions of the Cuban endemic toad Peltophryne fustiger: ψ-bufarenogin(Pseudobufarenogin), gamabufotalin, bufarenogin, arenobufagin, 3-(N-suberoylargininyl) marinobufagin, bufotalinin, telocinobufagin, marinobufagin and bufalin. In addition, the secretion was analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS which also allowed the identification of azelayl arginine. The effect of arenobufagin, bufalin and ψ-bufarenogin(Pseudobufarenogin) on Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase activity in a human kidney preparation was evaluated. These bufadienolides fully inhibited the Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase in a concentration-dependent manner, although arenobufagin (IC50 = 28.3 nM) and bufalin (IC50 = 28.7 nM) were 100 times more potent than ψ-bufarenogin (Pseudobufarenogin,IC50 = 3020 nM).
CONCLUSIONS:
These results provided evidence about the importance of the hydroxylation at position C-14 in the bufadienolide skeleton for the inhibitory activity on the Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase.
Oncotarget. 2015 May 10;6(13):11627-39.
ψ-Bufarenogin, a novel anti-tumor compound, suppresses liver cancer growth by inhibiting receptor tyrosine kinase-mediated signaling.
Resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) to existing chemotherapeutic agents largely contributes to the poor prognosis of patients, and discovery of novel anti-HCC drug is in an urgent need.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Herein we report ψ-Bufarenogin(Pseudobufarenogin), a novel active compound that we isolated from the extract of toad skin, exhibited potent therapeutic effect in xenografted human hepatoma without notable side effects. In vitro, ψ-Bufarenogin suppressed HCC cells proliferation through impeding cell cycle progression, and it facilitated cell apoptosis by downregulating Mcl-1 expression. Moreover, ψ-Bufarenogin decreased the number of hepatoma stem cells through Sox2 depression and exhibited synergistic effect with conventional chemotherapeutics. Mechanistic study revealed that ψ-Bufarenogin impaired the activation of MEK/ERK pathway, which is essential in the proliferation of hepatoma cells. ψ-Bufarenogin notably suppressed PI3-K/Akt cascade, which was required in ψ-Bufarenogin-mediated reduction of Mcl-1 and Sox2. ψ-Bufarenogin inhibited the auto-phosphorylation and activation of epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) and hepatocyte growth factor receptor (c-Met), thereafter suppressed their primary downstream cascades Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3-K/Akt signaling.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, ψ-Bufarenogin suppressed HCC growth via inhibiting, at least partially, receptor tyrosine kinases-regulated signaling, suggesting that ψ-Bufarenogin could be a novel lead compound for anti-HCC drug.