
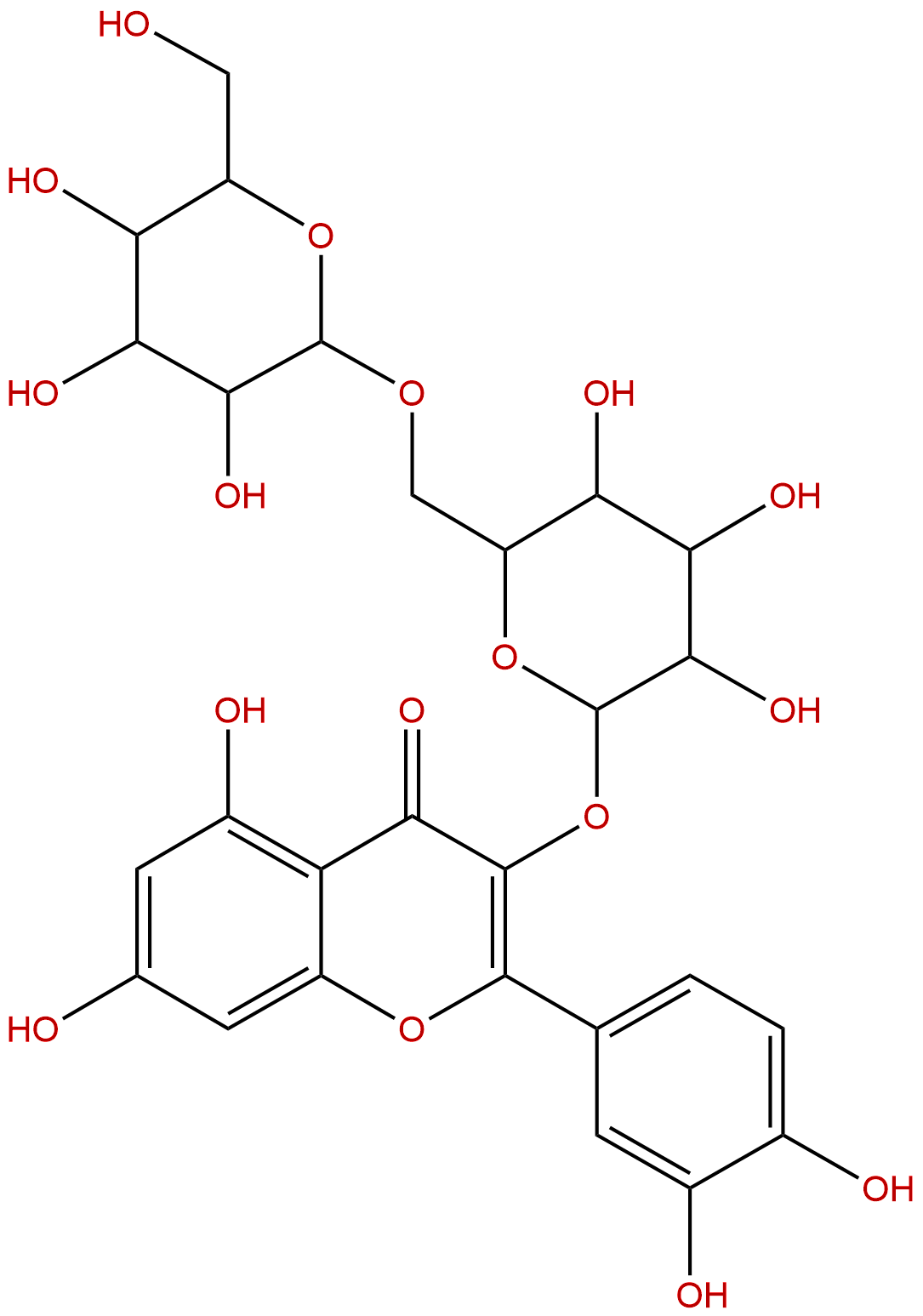
Quercetin 3-gentiobiosideCAS No.:7431-83-6 |
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1477 |
| Formula: | C27H30O17 |
| Mol Weight: | 626.52 |
Product name: Quercetin 3-gentiobioside
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1477
Cas No.: 7431-83-6
Formula: C27H30O17
Mol Weight: 626.52
Botanical Source:
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Quercetin-3-gentiobioside may show significant inhibitor on AR and AGEs formation activities.
References:
Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7375615.
Inhibitory Effect of Chemical Constituents Isolated from Artemisia iwayomogi on Polyol Pathway and Simultaneous Quantification of Major Bioactive Compounds.
Blocking the polyol pathway plays an important role preventing diabetic complications. Therefore, aldose reductase (AR) and advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs) formation has significant effect on diabetic complications. Artemisia iwayomogi has long been used as treatment of various diseases in Korea. However, no literatures have reported on AR and AGEs formation inhibitory activities of A. iwayomogi.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
For these reasons, we aimed to assess that A. iwayomogi had potential as anti-diabetic complications agents. We led to isolation of two coumarins (1 and 2), nine flavonoids (3-11), five caffeoylquinic acids (12-16), three diterpene glycosides (17-19), and one phenolic compound (20) from A. iwayomogi. Among them, hispidulin (4), 6-methoxytricin (6), arteanoflavone (7), Quercetin-3-gentiobioside (10), 1,3-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (13), and suavioside A (18) were first reported on the isolation from A. iwayomogi. Not only two coumarins (1 and 2), nine flavonoids (3-11), and five caffeoylquinic acids (12-16) but also extracts showed significant inhibitor on AR and AGEs formation activities. We analyzed contents of major bioactive compounds in Korea's various regions of A. iwayomogi.
CONCLUSIONS:
Overall, we selected Yangyang, Gangwon-do, from June, which contained the highest amounts of bioactive compounds, as suitable areas for cultivating A. iwayomogi as preventive or therapeutic agent in the treatment of diabetic complications.