
SauchinoneCAS No.:177931-17-8 |
||||||||||
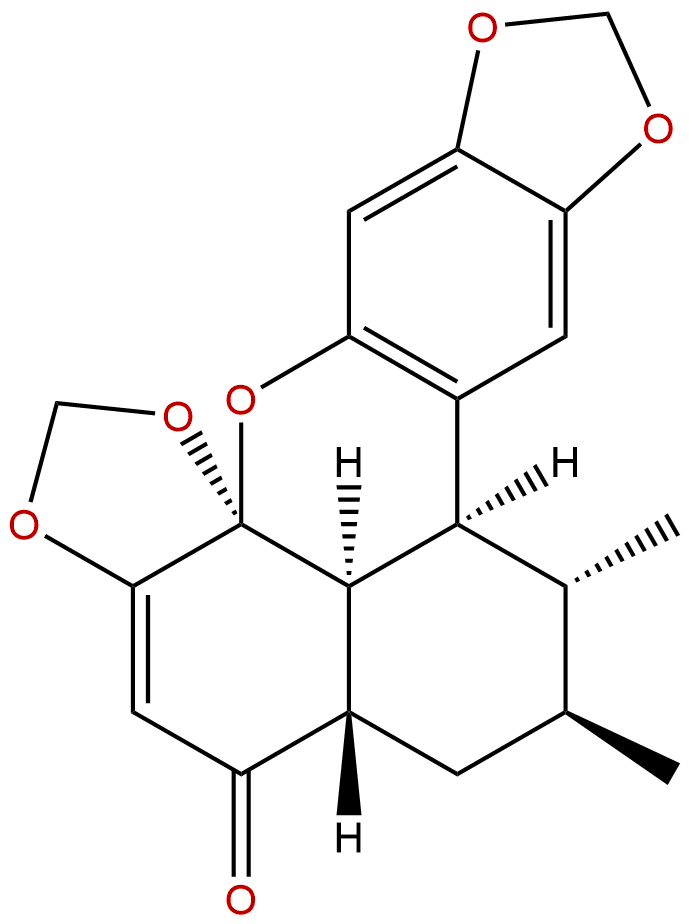 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1258 |
| Formula: | C20H20O6 |
| Mol Weight: | 356.374 |
| Botanical Source: | Saururus chinensis(Lour.)Baill |
Product name: Sauchinone
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1258
Cas No.: 177931-17-8
Formula: C20H20O6
Mol Weight: 356.374
Botanical Source: Saururus chinensis(Lour.)Baill
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Diterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Sauchinone possesses diverse pharmacological properties, such as hepatoprotective, neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects. Sauchinone protects skin keratinocytes through inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling via upregulation of oxidative defense enzymes. Sauchinone can be used for the prevention of functional β-cell damage, it prevents cytokine-induced NO production, iNOS expression,JAK/STAT activation,and NF-κB activation and inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS).
References:
Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Oct;17(2):471-7.
Sauchinone, a lignan from Saururus chinensis, attenuates neutrophil pro-inflammatory activity and acute lung injury.
Previous studies have shown that Sauchinone modulates the expression of inflammatory mediators through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways in various cell types. However, little information exists about the effect of Sauchinone on neutrophils, which play a crucial role in inflammatory process such as acute lung injury (ALI).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We found that Sauchinone decreased the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated murine bone marrow neutrophils, but not ERK1/2 and JNK. Exposure of LPS-stimulated neutrophils to Sauchinone or SB203580, a p38 inhibitor, diminished production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-2 compared to neutrophils cultured with LPS. Treatment with Sauchinone decreased the level of phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 (rpS6) in LPS-stimulated neutrophils. Systemic administration of Sauchinone to mice led to reduced levels of phosphorylation of p38 and rpS6 in mice lungs given LPS, decreased TNF-α and MIP-2 production in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, and also diminished the severity of LPS-induced lung injury, as determined by reduced neutrophil accumulation in the lungs, wet/dry weight ratio, and histological analysis.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Sauchinone diminishes LPS-induced neutrophil activation and ALI.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
Sauchinone, a lignan from Saururus chinensis, protects human skin keratinocytes against ultraviolet B-induced photoaging by regulating the oxidative defense system.
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight induces matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression, which are responsible for collagenous extracellular matrix proteins breakdown in skin, causing photoaging. Sauchinone is reported to have various bioactivity such as antioxidative, hepatoprotective, and anti-inflammatory effects. In the present study, we investigated the protective effect of Sauchinone against UVB (50 mJ/cm(2))-induced photoaging in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Sauchinone, at 5-40 μM, significantly protected keratinocytes against UVB-induced damage as assessed by cell viability and toxicity assay. Additionally, Sauchinone, at 20-40 μM, prevented the upregulation of MMP-1 proteins and reduction of type 1 collagen induced by UVB. Other assays revealed that, in keratinocytes, Sauchinone decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and increased glutathione levels and heme oxygenase-1. Sauchinone also inhibited UVB-induced phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrated that Sauchinone protects skin keratinocytes through inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling via upregulation of oxidative defense enzymes.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2003 Oct;26(10):1428-30.
Sauchinone, a lignan from Saururus chinensis, inhibits staurosporine-induced apoptosis in C6 rat glioma cells.
Neuronal apoptosis may contribute to pathologic neuronal loss in certain disease states such as neurodegenerative diseases. Staurosporine (ST), a nonselective protein kinase inhibitor, has been shown to induce apoptosis in a variety of cells including nerve cell lines. In this study, we investigated the neuroprotective effect of Sauchinone, which is a unique lignan from Saururus chinensis, on ST-induced apoptosis in C6 rat glioma cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Sauchinone attenuated ST-induced apoptosis of C6 glioma cells as evidenced by DNA fragmentation. We also provide evidence that the inhibitory effect of Sauchinone on ST-induced apoptosis involves a dose-dependent upregulation of an antiapoptotic protein, Bcl-2. Mounting evidence shows that the activation of caspases, especially caspase-3, triggers the apoptotic process. The activity of caspase-3 of ST-pretreated cells was significantly decreased upon Sauchinone treatment in a dose-dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the data demonstrate that Sauchinone protects C6 glioma cells from ST-induced apoptosis in a caspase-3 dependent manner. Our findings may be critical for developing a strategy to protect nerve cells from apoptosis, suggesting the potential development of Sauchinone as a neuroprotective agent.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Apr 5;728:176-82.
Effect of sauchinone, a lignan from Saururus chinensis, on bacterial phagocytosis by macrophages.
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays an important role in inflammation in various cells and increases the phagocytic ability of macrophages.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we found that Sauchinone increased the phosphorylation of AMPK and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), a downstream target of AMPK, in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Sauchinoneincreased macrophage phagocytosis of fluorescent Escherichia coli, which was blocked by compound C, an AMPK inhibitor. Sauchinone also increased the phosphorylation of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) in cultured macrophages in a concentration-dependent fashion, which was not blocked by compound C. However, the increase of Sauchinone-induced phagocytosis was prevented by SB203580. An inhibitor of the upstream kinase TGF-beta-activated kinase (TAK1), (5z)-7-oxozeaenol, abolished the phosphorylation of ACC and p38 MAPK. Systemic administration of Sauchinone to mice led to increased phosphorylation of AMPK and p38 MAPK in the lung, and enhanced phagocytosis of fluorescent E. coli in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid as compared with control mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest Sauchinone to be a useful adjunctive treatment for bacterial infection.