
SophoridineCAS No.:6882-68-4 |
||||||||||
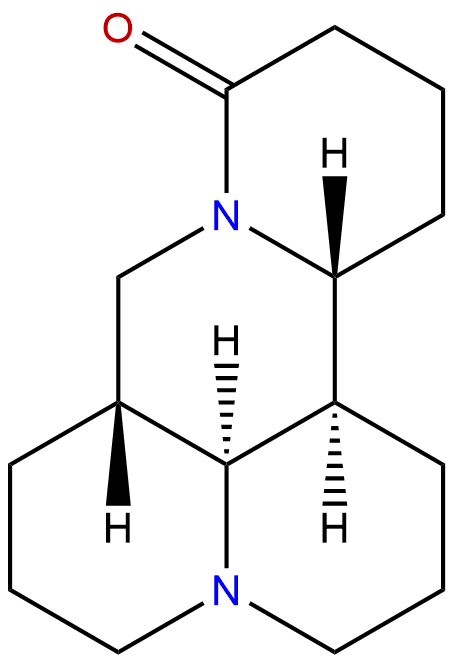 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1327 |
| Formula: | C15H24N2O |
| Mol Weight: | 248.37 |
| Botanical Source: | Sophora alopecuroides L |
Product name: Sophoridine
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1327
Cas No.: 6882-68-4
Formula: C15H24N2O
Mol Weight: 248.37
Botanical Source: Sophora alopecuroides L
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Alkaloids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Sophoridine has anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and anti-arrhythmia, and affects the immune and central nervous systems. Early and short-time applying sophoridine has neuroprotective effect min permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO) rat brain by down-regulating TRAF6 and up-regulating p-ERK1/2 expression, ameliorating brain infaction and edema. Sophoridine also possesses antiviral activities against Coxsackievirus B3, by regulating cytokine expression, may represent a potential therapeutic agent for viral myocarditis.
References:
Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015 May;31(5):585-9.
Sophoridine suppresses inflammatory cytokine secretion by lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells and its mechanism.
To observe the effects of Sophoridine on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced secretion of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and interleukin 1β (IL-1β) as well as the expressions of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and c-Jun in RAW264.7 cells and explore the molecular mechanism of anti-LPS of Sophoridine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
RAW264.7 cells were cultured and divided into four groups: macrophage control group (using serum-free DMEM to incubate cells), Sophoridine control group (using 31.25 mg/L Sophoridine-added DMEM to incubate cells), LPS group and Sophoridine intervention group (using 100 μg/L LPS DMEM to incubate cells for 60 minutes, then throwing away LPS and adding serum-free DMEM or 31.25 mg/L Sophoridine DMEM to incubate cells). Cells and culture medium were collected respectively at 5, 30, 60 and 120 minutes after the above treatment. The expression levels of TLR4 and c-Jun mRNA were determined by reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), and the expression of c-Jun protein in RAW264.7 cells was measured by immunocytochemistry and Western blotting; The levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in cell culture medium were analyzed by ELISA. Compared with macrophage control group, Sophoridine control group had no statistical difference in each index. Compared with macrophage control group, the expressions of TLR4 mRNA, c-Jun mRNA and protein as well as the secretion of TNF-α and IL-1β significantly increased at each time point in LPS group, and maintained the level to 120 minutes. Sophoridine suppressed the expressions of TLR4 mRNA, c-Jun mRNA and protein, and reduced the secretion of TNF-α and IL-1β in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells in Sophoridine intervention group.
CONCLUSIONS:
Sophoridine down-regulated the secretion of TNF-α and IL-1β in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells via inhibiting the expressions of TLR4 and c-Jun.
Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1999 Jun;20(6):517-20.
Anti-arrhythmic effects of sophoridine and oxysophoridine.
To compare the effects of oxySophoridine (Oxy) and Sophoridine (Sop) on experimental arrhythmias and myocardial physiologic properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Arrhythmias were induced by drugs and myocardial ischemia. Physiologic properties were determined on isolated heart atria. Oxy 500 mg.kg-1 (1/6 LD50) decreased the incidence of ventricular arrhythmias induced by aconitine (P < 0.01), increased the threshold dose of ouabain-induced ventricular premature (VP, P < 0.05), ventricular tachycardia (VT, P < 0.05), ventricular fibrillation (VF, P < 0.01), and cardiac arrest, (P < 0.01). After i.v. Oxy 500 mg.kg-1 into the rats with ligation of left anterior descending coronary artery, the total numbers of ectopic beats were decreased (P < 0.05), the incidence of VF was lowered, and the duration of VT was shortened (P < 0.01). Oxy 250 mg.kg-1 (1/13 LD50) i.v. shortened the duration of arrhythmias induced by BaCl2 (P < 0.01) and delayed the onset of arrhythmias induced by chloroform-epinephrine (P < 0.05). Oxy produced dose-dependent positive inotropic effects in the isolated left atrial of guinea pigs, increased the concentration of epinephrine to elicit automaticity in left atria, decreased slightly the excitability, and prolonged the functional refractory period. Sop produced the similar effects on arrhythmias as Oxy.
CONCLUSIONS:
Oxy produced the similar anti-arrhythmic effects as Sop did at the equivalent effective dose.