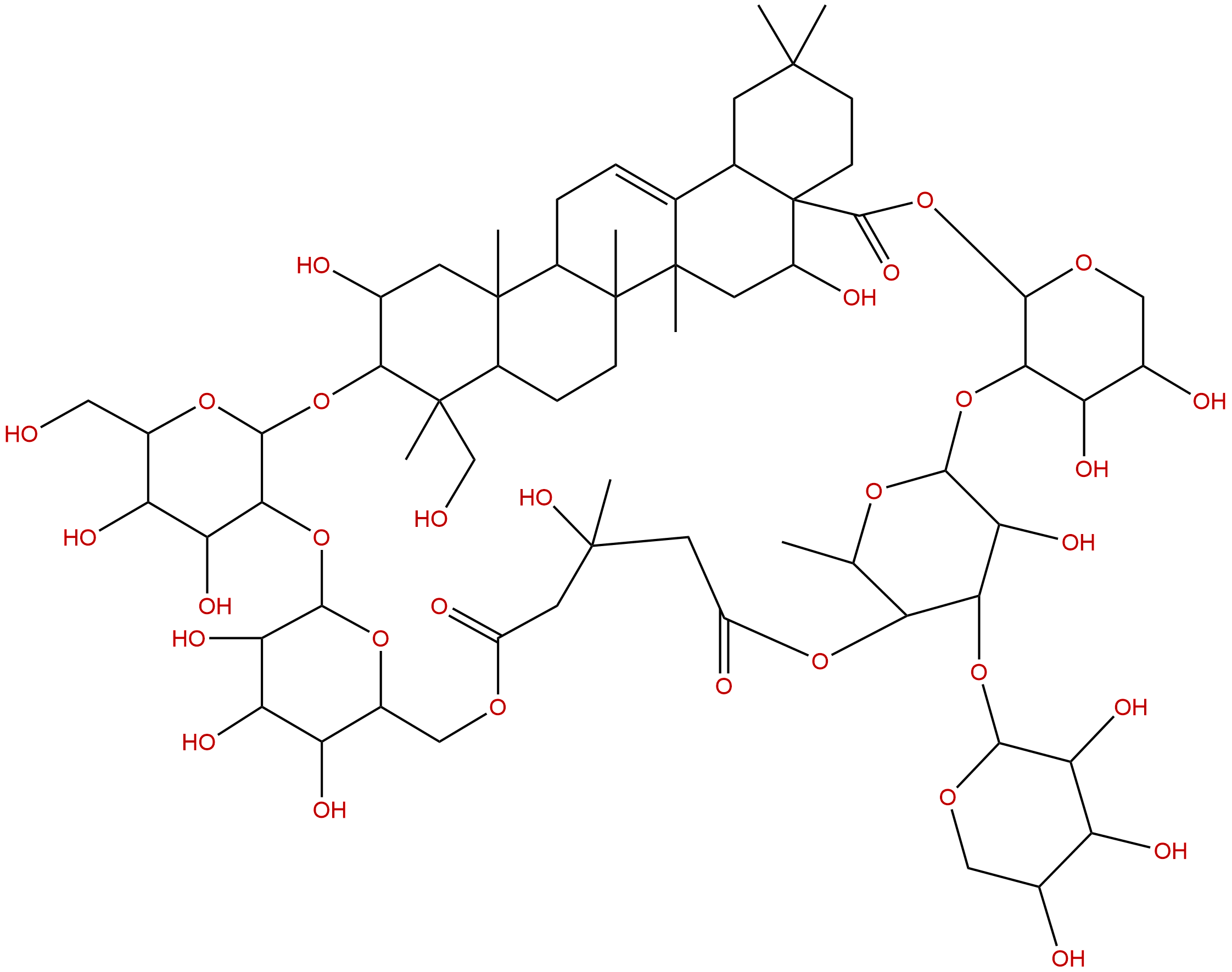
Tubeimoside IIICAS No.:115810-13-4 |
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1482 |
| Formula: | C64H100O31 |
| Mol Weight: | 1365.47 |
| Botanical Source: | Bolbostemma paniculatum(Maxim.) Franquet |
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1482
Cas No.: 115810-13-4
Formula: C64H100O31
Mol Weight: 1365.47
Botanical Source: Bolbostemma paniculatum (Cucurbitaceae)
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Tubeimoside III has anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and anti-tumorigenic activities, stronger than those of tubeimoside II. It has acute toxicity, stronger than that of tubeimoside II.
References:
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2001 May;22(5):463-8.
Structure-activity relationship of tubeimosides in anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and antitumor-promoting effects.
To study structure-activity relationship of tubeimosides isolated from Bolbostemma paniculatum for their anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and antitumor-promoting effects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Tubeimoside I, Tubeimoside II, and Tubeimoside III were isolated from tubers of Bolbostemma paniculatum (Maxim) Franquet (Cucurbitaceae), a Chinese folk medicine,"Tubeimu", and their anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, anti-tumorigenic activities, and acute toxicity were studied in vivo. Tubeimoside I, Tubeimoside II, and Tubeimoside III are all natural analogues of oleanane type of triterpenoid saponins from the same medicinal plant, and all show anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and antitumor-promo ting effects. However, the anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and anti-tumorigenic activities of Tubeimoside II are stronger than those of tubeimoside I, and the acute toxicity of Tubeimoside II is lower than that of tubeimoside I; the anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and anti-tumorigenic activities of Tubeimoside III are stronger than those of Tubeimoside II, and the acute toxicity of Tubeimoside III is also stronger than that of Tubeimoside II.
CONCLUSIONS:
C-16 hydroxyl group of Tubeimoside II plays an important role in enhancing biological activity of Tubeimoside II and in decreasing its toxicity. The difference of chemical structure in B and/or C position between tubeimosides III and II plays an important role in enhancing biological activity and toxicity of Tubeimoside III. Therefore tubeimosidre II may be the most promising agent for cancer chemoprevention and chemotherapy among tubeimosides I, II, and III.
Carcinogenesis. 1995 Dec;16(12):3045-8.
Inhibition of the tumor promoting action of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate by tubeimoside III isolated from Bolbostemma paniculatum.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
As tubeimoside I isolated from Bolbostemma paniculatum (Maxim.) Franquet (Cucurbitaceae) has been shown to suppress tumor promoter effects, Tubeimoside III from the same plant was tested in vitro and in vivo against the action of the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA). Tubeimoside III, the natural analog of tubeimoside I, also had an anti-inflammatory effect on mouse ear edema induced by arachidonic acid and TPA and a potent anti-tumor promoting effect on two-stage carcinogenesis of mouse skin after topical application. However, the important difference in bioactivities between tubeimosides I and III is the non-activity of Tubeimoside III as an inhibitor of tumor promotion if administered orally.
CONCLUSIONS:
Differences in metabolism connected with different routes of the compound may be one of a number of explanations of the important difference.
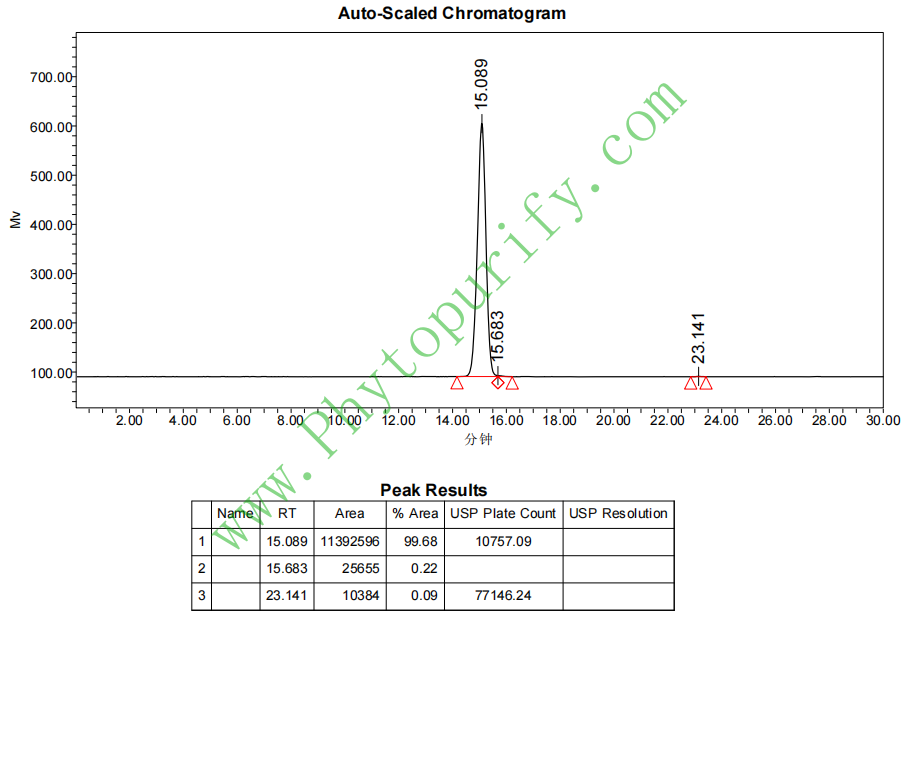
HPLC of Tubeimoside III