
Epimagnolin BCAS No.:1134188-26-3 |
||||||||||
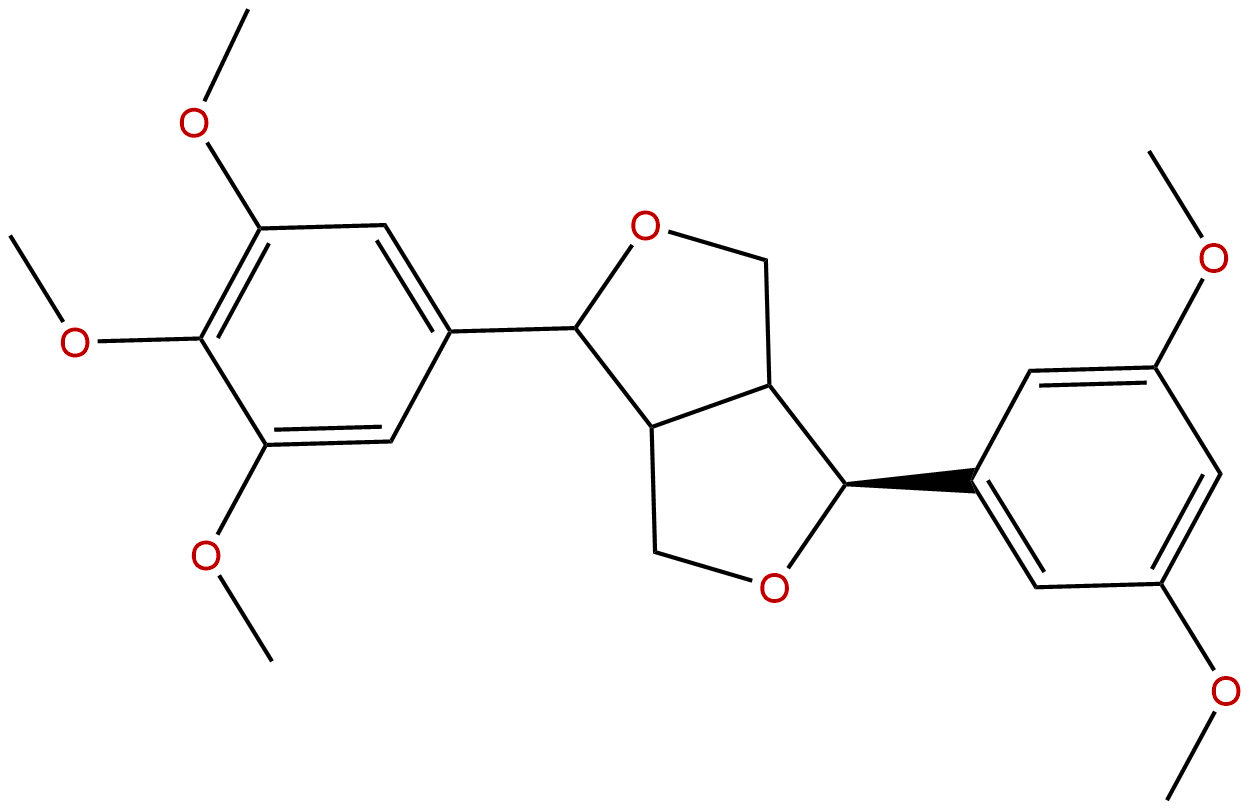 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1775 |
| Formula: | C23H28O7 |
| Mol Weight: | 416.47 |
Product name: Epimagnolin B
Synonym name: CHEMBL480759
Catalogue No.: BP1775
Cas No.: 1134188-26-3
Formula: C23H28O7
Mol Weight: 416.47
Botanical Source: Flower of Magnolia liliiflora Desr.
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Lignans
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
We provide solution to improve the water-solubility of compounds, thereby facilitating the variety of activity tests and clinic uses.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Epimagnolin B has anti-inflammatory activity, it can inhibit the production of NO and PGE(2) and the expression of respective enzyme iNOS and COX-2 through the suppression of I-kappaB-alpha degradation and nuclear translocation of p65 subunit of NF-kappaB. It also exhibits antiallergic effects without affecting the viability of bone marrow-derived mast cells.
References:
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Feb 1;19(3):937-40.
In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of lignans isolated from Magnolia fargesii.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The overproduction of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) causes neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Four lignans, (+)-eudesmin (1), (+)-magnolin (2), (+)-yangambin (3) and a new structure named as Epimagnolin B (4) were isolated from Magnolia fargesii (Magnoliaceae) as the inhibitors of NO production in LPS-activated microglia.
CONCLUSIONS:
The most potent compound 4 inhibited the production of NO and PGE(2) and the expression of respective enzyme iNOS and COX-2 through the suppression of I-kappaB-alpha degradation and nuclear translocation of p65 subunit of NF-kappaB.
Rsc Advances, 2017, 7(54):34236-34243.
Bioassay-guided isolation of bisepoxylignans from the flower buds of Magnolia biondii Pamp and their antiallergic effects.
The dried flower buds of Magnolia biondii Pamp (herbal name, Xin-Yi) are a traditional Chinese medicine with a long history of clinical use in the treatment of allergic rhinitis and sinusitis. However, the constituents responsible for its antiallergic effects remain unidentified.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, a novel bisepoxylignan, isoeudesmin (1), and eight known bisepoxylignans, pluviatilol (2), eudesmin (3), magnolin (4), lirioresinol-B dimethyl ether (5), Epimagnolin B (6), kobusin (7), aschantin (8), fargesin (9), were isolated from effective fractions through antiallergic bioassay-guided procedures using mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) and IgE-induced passive cutaneous anaphylaxis mice. The compound structures were elucidated through nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry analyses. Compound 1 and compounds 2–6 and 9 exhibited antiallergic effects without affecting the viability of BMMCs. Compounds 2 and 9 showed the strongest effects with IC50 values of 52.18 and 93.03 μM, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
In this paper, the structure–activity relationship between these bisepoxylignans and their antiallergic effects is discussed. After evaluating the intensity of the antiallergic effects of the extracts, further separating the fractions, and isolating the purified compounds, we concluded that biosepoxylignans are the main constituents in Xin-Yi contributing to its anti-allergic efficacy.