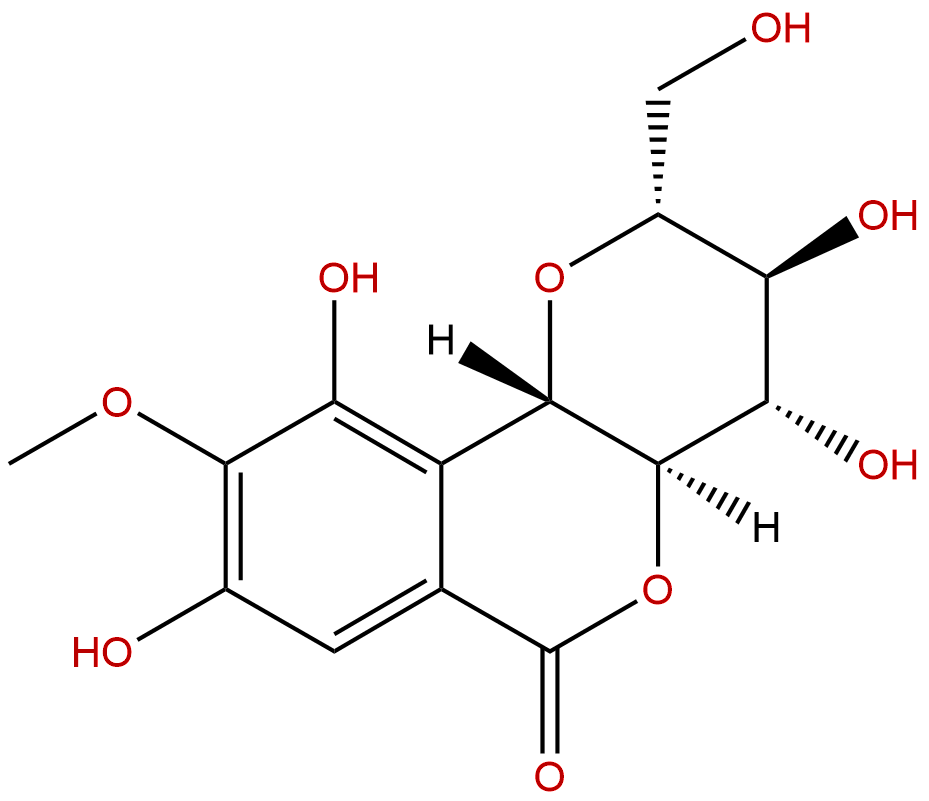
BergeninCAS No.:477-90-7
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0258 |
| Formula: | C14H16O9 |
| Mol Weight: | 328.273 |
Product name: Bergenin
Synonym name: Ardisic acid B; Ardisinic acid; Bergenitol; Corylopsin; Cuscutin; Peltophorin; Vakerin
Catalogue No.: BP0258
Cas No.: 477-90-7
Formula: C14H16O9
Mol Weight: 328.273
Botanical Source: Bergenia purpurascens
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Phenols
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Bergenin is a potent antinarcotic agent, has antiviral ,antifungal, antiarrhythmic, antitumor, antiinflammatory, potent immunomodulatory, antitussive, antiulcerogenic,anti-plasmodial, anti-hepatotoxic and wound healing activities. Bergenin has antidiabetic activity, could be classified as a new group of α-glucosidase inhibitors. Bergenin reduces the expression of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 proinflammatory cytokines by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways, and it may represent a novel treatment strategy for mastitis.
References:
Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Jun;38(6):1248-54.
Bergenin decreases the morphine-induced physical dependence via antioxidative activity in mice.
Oxidative stress plays a role in the development of physical dependence induced by morphine. Bergenin, a polyphenol found in many Asian, African, and South American medicinal plants, is a potent antinarcotic agent with wide spectrum of pharmacological activities including antioxidant action.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we observed that Bergenin decreased the development of physical dependence induced by morphine in mice and the antioxidant activity of Bergenin plays a role in the antinarcotic effects through adapting to morphine-induced oxidative stress in the brain. The naloxone-precipitated withdrawal symptom (jumping frequency) was significantly ameliorated (50% of control group) by administration of Bergenin (20 mg/kg) in morphine-treated mice. Furthermore, morphine-induced down-regulation of glutathione (GSH) contents was reversed by Bergeninadministration in the frontal cortex and liver. Bergenin had no effects on the increased levels of nfr2-dependent antioxidant enzyme HO1 and NQO1 in the frontal cortex, striatum, and liver of morphine-treated mice. However, the morphine-induced increase in nrf2 nuclear translocation in the frontal cortex and striatum was inhibited by Bergenin treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Bergenin has a potential antinarcotic effect via regulation of GSH contents and oxidative stress.
Fitoterapia. 2015 Mar;101:133-52.
Diversity, pharmacology and synthesis of bergenin and its derivatives: potential materials for therapeutic usages.
Bergenin, a natural secondary metabolite, has been isolated from different parts of a number of plants. It is one of active ingredients in herbal and Ayurvedic formulations. It exhibits antiviral, antifungal, antitussive, antiplasmodial, antiinflammatory, antihepatotoxic, antiarrhythmic, antitumor, antiulcerogenic, antidiabetic and wound healing properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
It has been analyzed and estimated in different plant extracts, blood and drug samples using chromatographic techniques, and pharmacokinetic studies have been made. Several Bergeninderivatives were isolated and/or synthesized and were found to possess pharmacological activities. Total synthesis of Bergenin and its derivatives were reported. This review article covers literature on Bergenin and its derivatives until 2013. Ethnomedicinal value of Bergenin containing plant materials is also highlighted.
CONCLUSIONS:
This comprehensive review provides information on the potentiality of Bergenin and its derivatives for therapeutic usages.
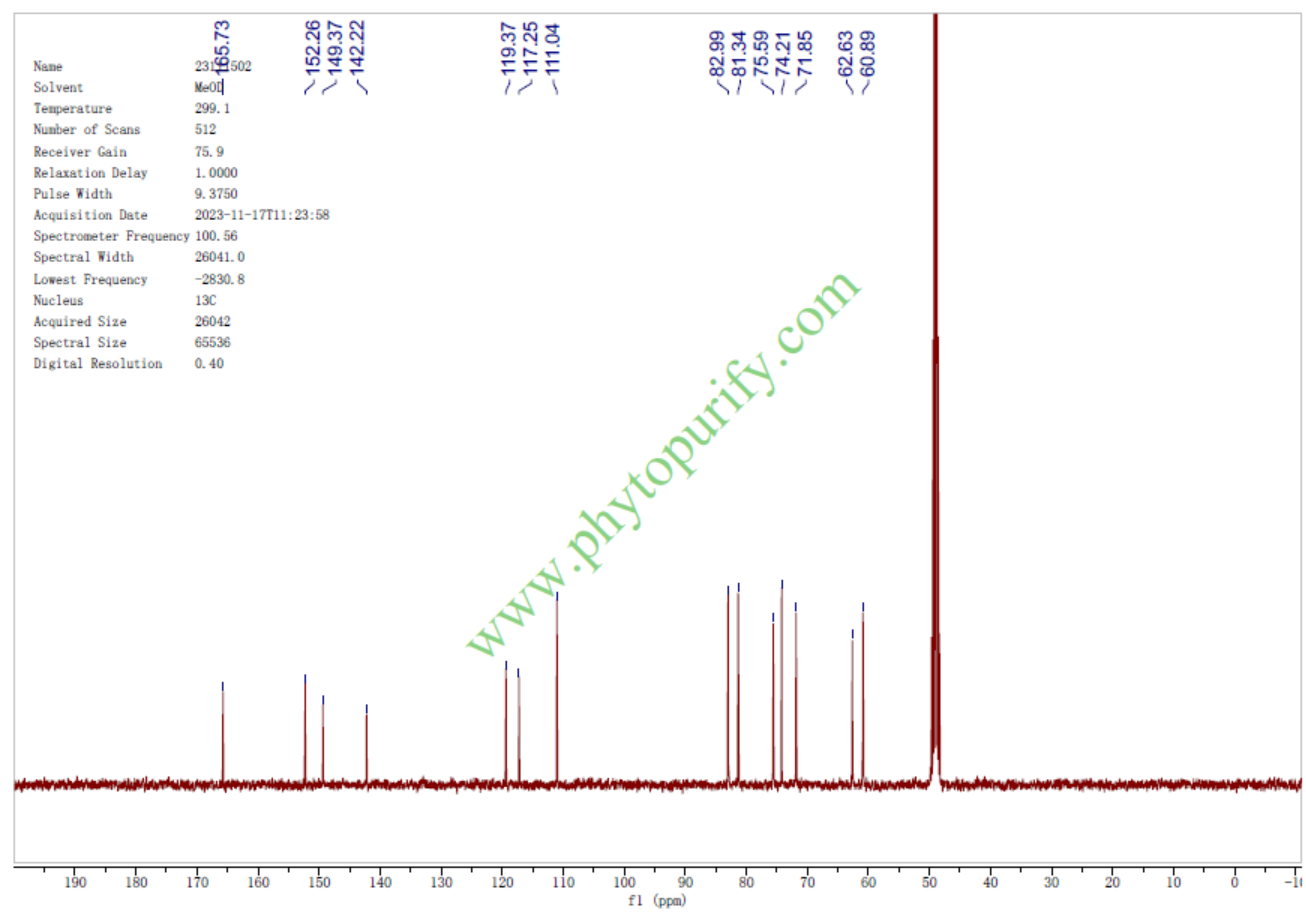
NMR of Bergenin
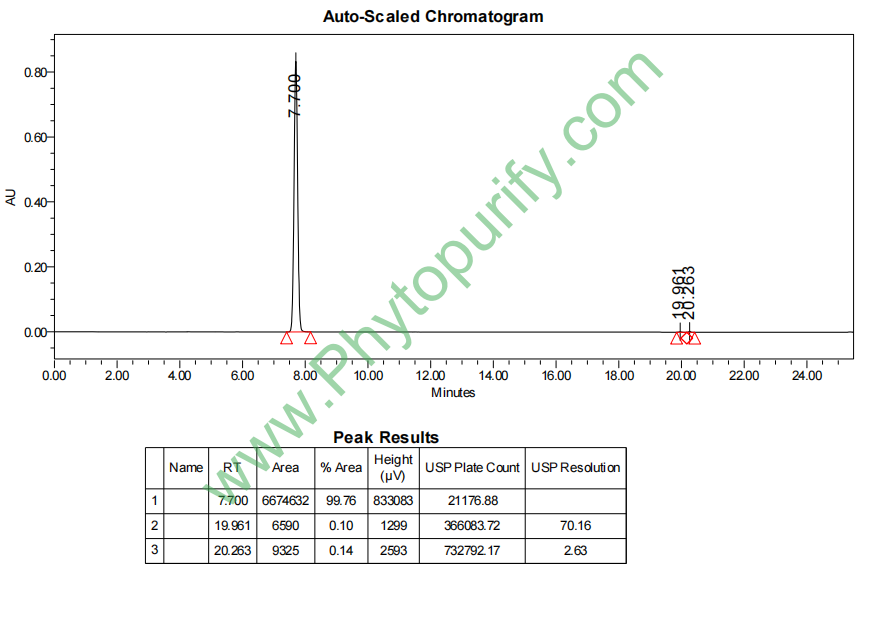
HPLC of Bergenin