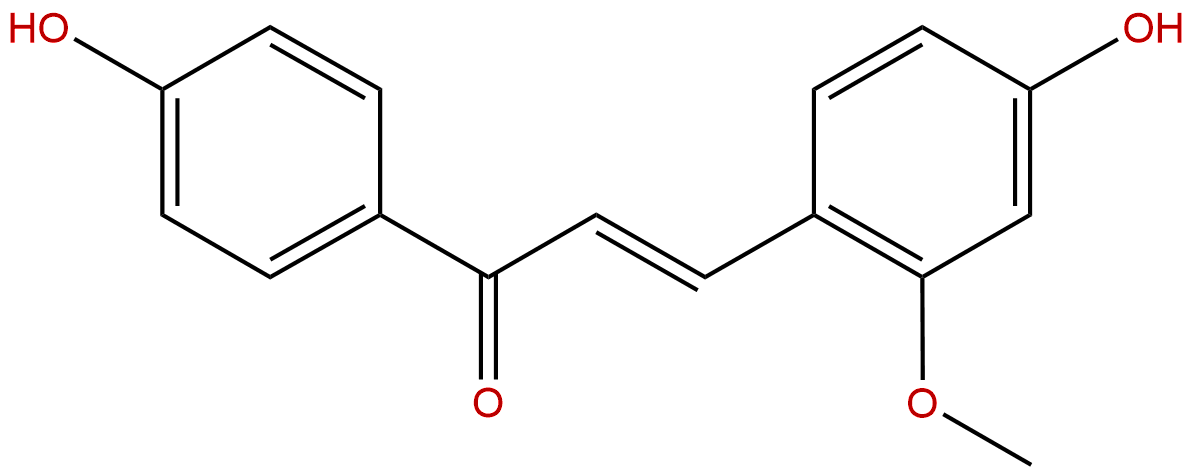
EchinatinCAS No.:34221-41-5
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0521 |
| Formula: | C16H14O4 |
| Mol Weight: | 270.284 |
Synonym name: 4'-Dihydroxy-2-methoxychalcone
Catalogue No.: BP0521
Cas No.: 34221-41-5
Formula: C16H14O4
Mol Weight: 270.284
Botanical Source: tissue culture of Glycyrrhiza echinata, from Glycyrrhiza inflata and Bauhinia manca
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Echinatin has significant antioxidant and anti-inflammary activities, it shows strong scavenging activity toward the ABTS + radical, it also inhibits the production of nitric oxide (NO), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in LPS-induced macrophage cells. Echinatin disturbs the mitochondrial energy transfer reactions and membrane permeability, at a low concentration cause deterioration of respiratory control and oxidative phosphorylation of isolated rat liver mitochondria, inhibits DNP-ATPase activity while stimulating range latent ATPase activity.
References:
J Toxicol Sci. 1982 Nov;7(4):245-54.
The effects of echinatin and its related compounds on the mitochondrial energy transfer reaction.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To investigate the mechanism by which various biological action of licorice root are brought about, the effects of Echinatin as a small constituent of Glycyrrhiza echinata and several related compounds on mitochondrial energy transfer reactions were examined. The results obtained were as follows: 1) Echinatin, 4'-hydroxychalcone, chalcone and 3,4'-dihydroxychalcone at a low concentration cause deterioration of respiratory control and oxidative phosphorylation of isolated rat liver mitochondria. 2) Chalcone and 4'-hydroxychalcone stimulate both latent and DNP-ATPase activity of mitochondria. Echinatin inhibits DNP-ATPase activity while stimulating range latent ATPase activity in the low concentration. 3) Chalcone and 4'-hydroxychalcone induce a rapid potassium release from mitochondrial vesicles, while Echinatin and 3,4'-dihydroxychalcone have lesser effect than the former two substances.
CONCLUSIONS:
From these results, it can be concluded that Echinatin and several related compounds disturb the mitochondrial energy transfer reactions and membrane permeability.
Food Chem. 2013 Nov 15;141(2):1063-71.
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of six flavonoids separated from licorice.
Licorice, the roots and rhizomes of several Glycyrrhiza species (Leguminosae), is an important natural sweetening agent and a widely used herbal medicine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, six flavonoids, 5-(1,1-dimethylallyl)-3,4,4'-trihydroxy-2-methoxychalcone (1), licochalcone B (2), licochalcone A (3), Echinatin (4), glycycoumarin (5) and glyurallin B (6), were isolated from the extracts of licorice (Glycyrrhiza inflata and Glycyrrhiza uralensis). Their structures were elucidated using various spectroscopic methods. To our knowledge, compound 1 was isolated from natural plants for the first time. All the isolates were tested by antioxidant and anti-inflammatory assays. Compounds 2, 4 and 5 showed strong scavenging activity toward the ABTS(+) radical, and compounds 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6 exhibited potent inhibition of lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes compared with the reference controls. Compounds 1-4 dose-dependently inhibited LPS induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in RAW 264.7 cells. Furthermore, compounds 1-5 were demonstrated to inhibit the production of nitric oxide (NO), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in LPS-induced macrophage cells. Moreover, the contents of the six compounds, in different Glycyrrhiza species, were quantified by HPLC-MS.
Chinese Journal of New Drugs, 2013, 22(21):2547-52.
Determination of antioxidant activity in licorice vitro metabolites by DPPH spiking coupled with HPLC-Q-TOF MS/MS
To investigate the antioxidant activity of liver microsomal metabolites from six flavonoids in licorice by 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) spiking coupled with HPLC-Q-TOF MS/MS.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The six flavonoids were incubated with rat liver microsomes and the resultant metabolites were identified by HPLC-Q-TOF MS/MS. The antioxidant activity of the metabolites was calculated by comparing the peak area changes before and after incubation with DPPH. The peak area of the metabolites significantly decreased or even disappeared after incubation with DPPH. Besides the metabolites Lico A-M1 and Lico A-M2 of licochalcone A, more than 90% of other metabolites of flavonoids were oxidized.
CONCLUSIONS:
Liver microsomal metabolites of Echinatin, licochalcone B, licochalcone A, 5-(1, 1-dimethylally)-3, 4, 4'-trihydroxy-2-methoxychalcone, glycycourmarin and glyurallin B still have significant antioxidant activities.
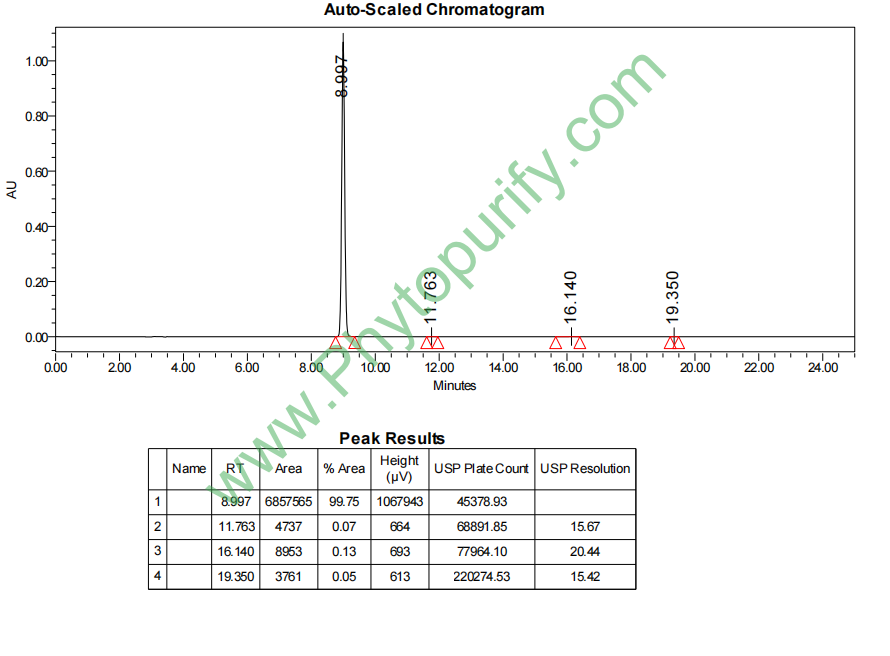
HPLC of Echinatin