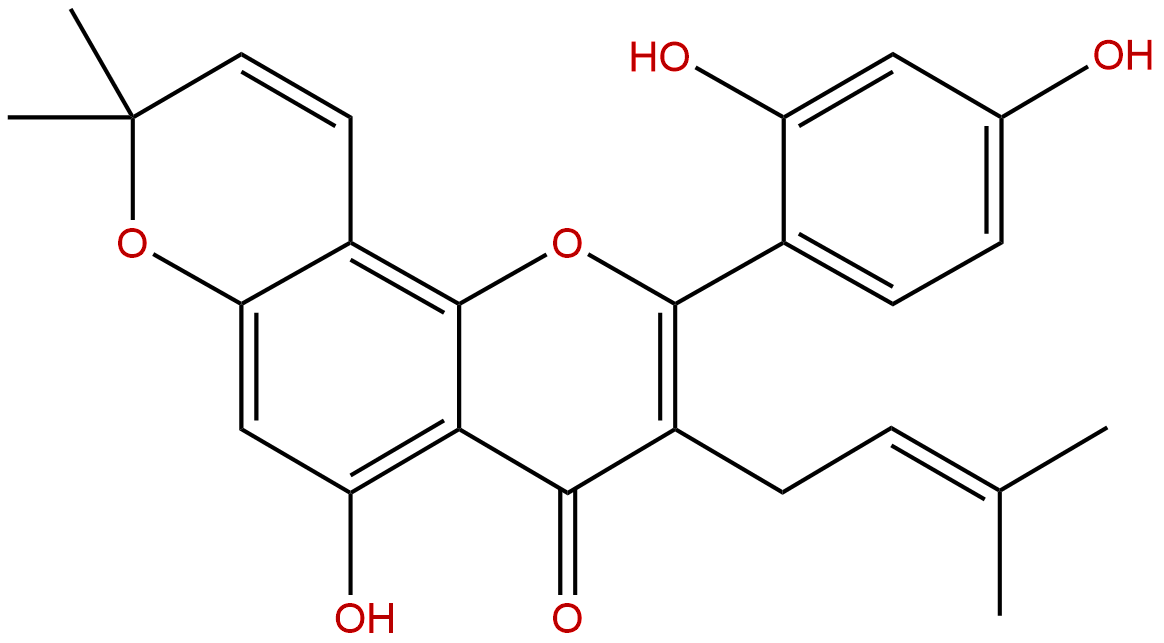
MorusinCAS No.:62596-29-6
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0961 |
| Formula: | C25H24O6 |
| Mol Weight: | 420.461 |
Product name: Morusin
Synonym name: Mulberrochromene
Catalogue No.: BP0961
Cas No.: 62596-29-6
Formula: C25H24O6
Mol Weight: 420.461
Botanical Source: Mori cotex
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Morusin exhibits antinociceptive, analgesic, anticonvulsant, antibacterial, and antitumor activities. Morusin can inhibit NF-κB and STAT3 activity, activate caspases activity, and restorate GABA level.
References:
Toxicol Lett. 2015 Jan 22;232(2):490-8.
Antitumor progression potential of morusin suppressing STAT3 and NFκB in human hepatoma SK-Hep1 cells.
Morusin is a prenylated flavonoid that has been isolated from the root bark of the mulberry tree (Morus species, Moraceae), a Chinese traditional medicine. It has been synthesized by our laboratory from commercially available phloroglucinol, and has demonstrated to possess antitumor effects of cell lines including A549, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, at non-cytotoxic concentrations, Morusin altered invasive morphology and suppressed cell-matrix adhesion, cell motility and cell invasion in SK-Hep1 cells. Morusin also increased the expression of E-cadherin, an epithelial cell junction protein, decreased the expression of vimentin, a mesecnchymal marker, and α2-, α6-, β1- integrin, which regulated cancer attachment and migration. In addition, Morusin reduced the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and 9 (MMP-2 and MMP-9), which were involved in extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation and promoting cancer cell invasion. Furthermore, Morusin suppressed the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and nuclear factor-κB (NFκB) signaling pathways, which modulate the protein expression involved in the invasion process. Finally, Morusin decreased the lung colonization of the SK-Hep1 cells in the nude mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate Morusin possesses antitumor progression potential through suppressing STAT3 and NFκB.
Mol Carcinog. 2014 Dec 31.
Morusin inhibits glioblastoma stem cell growth in vitro and in vivo through stemness attenuation, adipocyte transdifferentiation, and apoptosis induction.
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cancer stem cells (GSCs) are responsible for the progression and recurrence of GBM after conventional therapy. Morusin possesses anti-cancer activity in vitro. The purpose of this study is to confirm the growth inhibition effect of Morusin on human GSCs growth in vitro and in vivo and to explore the possible mechanism of its activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Human GSCs were enriched under nonadhesive culture system, and characterized through neurosphere formation, toluidine blue staining, immunofluorescence staining, Western blotting analysis of stemness markers of CD133, nestin, Sox2 and Oct4, and tumorigenecity in vivo; the growth inhibition effect of Morusin on human GSCs in vitro and in vivo were tested by cell cytotoxicity, neurosphere formation inhibition, adipogenic differentiation, apoptosis induction, and tumor growth inhibition in vivo assays. The potential molecular mechanisms underlying the growth inhibition effect of Morusin on GSCs in vitro and in vivo were investigated with Western blotting evaluation of stemness, adipogenic, and apoptotic proteins in Morusin treated GSCs and tumor tissues. GSCs enriched under nonadhesive culture system possess stemness characterstics; Morusin inhibited GSCs growth in vitro and in vivo, it reduced stemness of GSCs, induced them adipocyte-like transdifferention and apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Morusin has the potential to inhibit human GSCs growth in vitro and in vivo through stemness attenuation, adipocyte transdifferentiation, and apoptosis induction.
Science of Sericulture, 2013, 39(6):1150-4.
An Investigation on Antibacterial Activity and Stability of Morusin.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study,inhibitory effects of Morusin from mulberry( Morus L.) against 5 common food-borne pathogenic bacteria,namely Staphyloccocus aureus,Bacillus subtilis,Escherichia coli,Salmonella spp. and Proteus vulgaris,were tested by agar diffusion method and microscale double dilution method. Meanwhile,the effects of thermal treatment,ultraviolet illumination,medium pH value,oxidant and reducer on the antibacterial activity of Morusin were also investigated. The results indicated that inhibitory effects of Morusin against the 5 tested bacterial strains were different. The two Gram-positive bacteria( G+),Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus,were remarkably inhibited. Morusin had the highest antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis,with the minimum inhibitory concentration( MIC) below 1. 56μg /mL. Its inhibition to the three Gram-negative bacteria( G-),Salmonella spp.,P. vulgaris and E. coli,was relatively weak. Ultraviolet illumination and thermal treatment below 100 ℃ had no obvious influence on the antibacterial activity of Morusin. After thermal treatment of above100 ℃,the antibacterial activity of Morusin decreased obviously. Within pH 6 ~ 9 range,the antibacterial activity of Morusin decreased with increase of medium pH value.When the concentration of reducer Na2SO3was increased,the antibacterial activity of Morusin to Staphylococcus aureus declined gradually. The concentration of oxidant H2O2 had little influence on the antibacterial activity of Morusin.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Morusin is one of the important substances of mulberry with antibacterial activity. High temperature( above 100 ℃),strong alkaline and high concentration reducer had influence on the antibacterial activity of Morusin.
Z Naturforsch C. 2000 Mar-Apr;55(3-4):256-60.
Antinociceptive properties of morusin, a prenylflavonoid isolated from Morus nigra root bark.
The antinociceptive effects of Morusin (1), the main prenylflavonoid present in the Morus nigra root barks have been investigated in classical models of pain in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The results showed that 1 exhibits a promising antinociceptive or analgesic profile by the intraperitoneal route, being more potent than some standard drugs used as reference.
CONCLUSIONS:
The mechanism by which the Morusin exerts antinociceptive activity still remains undetermined, but our results strongly suggest that it involves the participation of the opioid system.
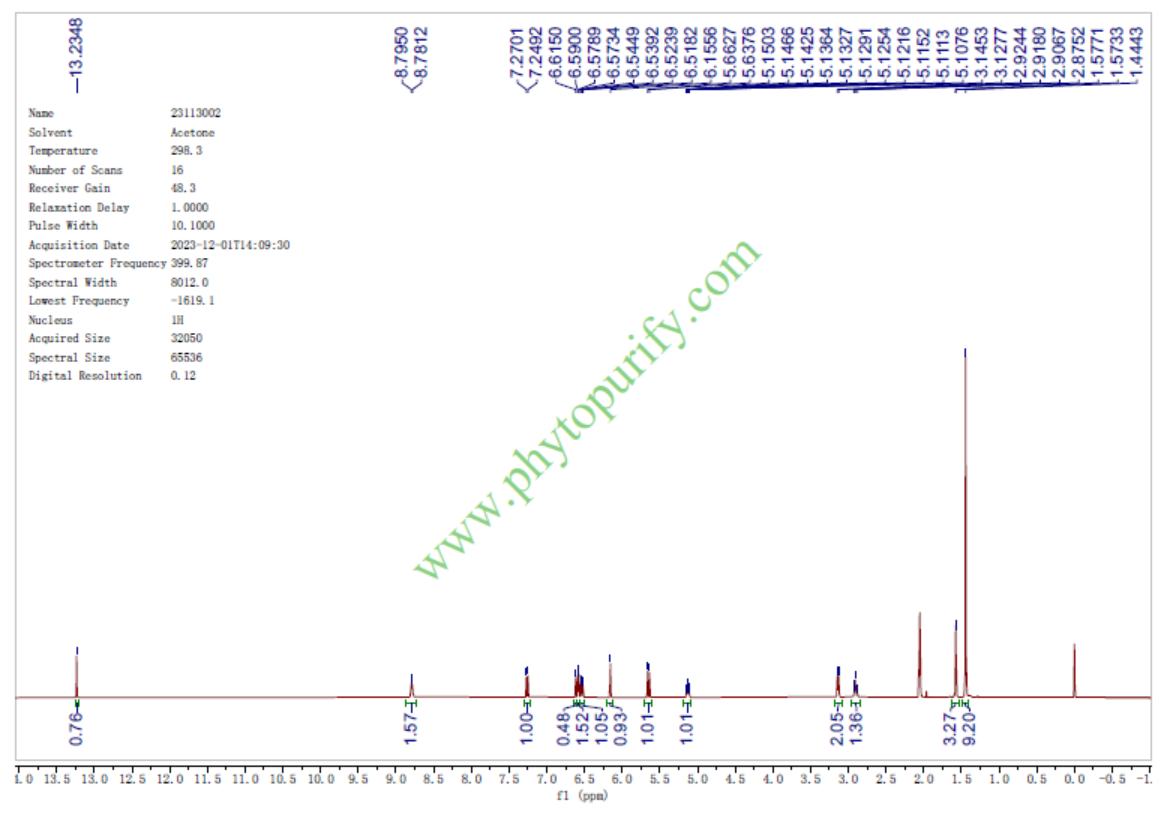
HNMR of Morusin
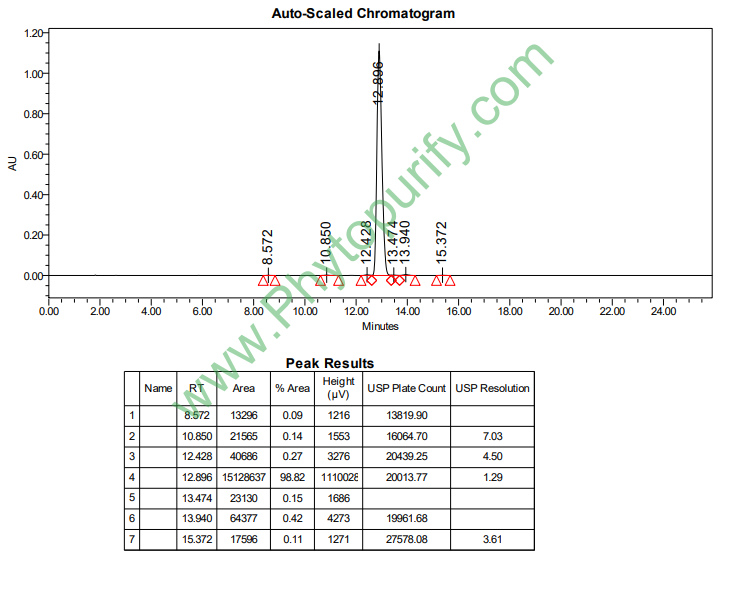
HPLC of Morusin