
Polygalic AcidCAS No.:1260-04-4 |
||||||||||
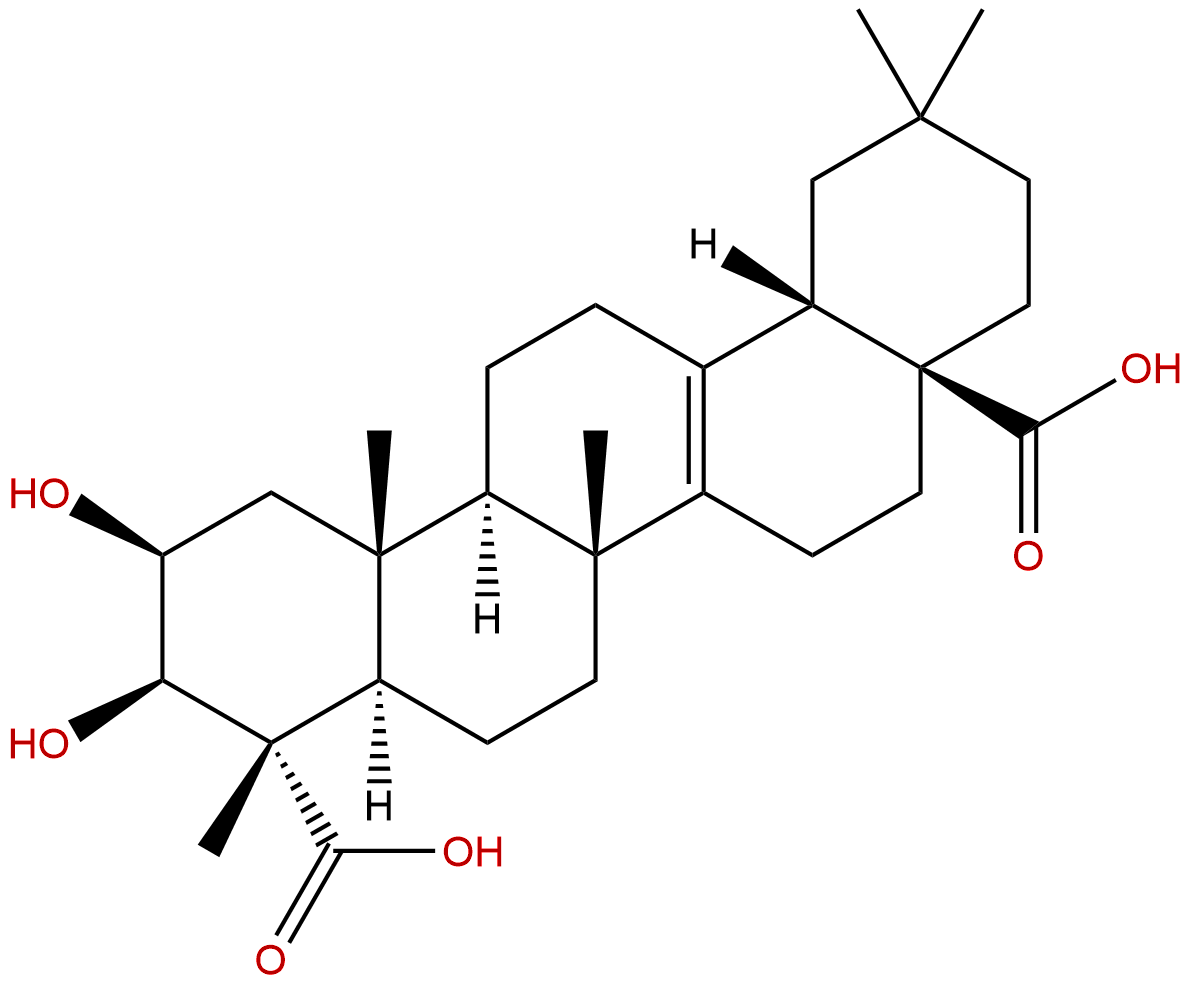 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP3322 |
| Formula: | C29H44O6 |
| Mol Weight: | 488.665 |
| Botanical Source: | Polygalae radix |
Product name: Polygalic Acid
Synonym name: Senegenic acid
Catalogue No.: BP3322
Cas No.: 1260-04-4
Formula: C29H44O6
Mol Weight: 488.665
Botanical Source:
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
We provide solution to improve the water-solubility of compounds, thereby facilitating the variety of activity tests and clinic uses.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Polygalic acid, a triterpenoid saponin, shows expectorant, emetic and stimulant effects.
References:
Biomed Chromatogr. 2012 Feb;26(2):220-4.
In vivo metabolism study of polygalic acid in rat using HPLC-ESI-MSn.
A very simple and direct method has been established for the determination of Polygalic acid and its metabolites in rat urine based on HPLC coupled with electrospray ionization multi-stage tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS(n)).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The rats were administered a single dose (100 mg/kg) of Polygalic acid by oral gavage. The urine samples were collected and purified through a C(18) solid-phase extraction cartridge, and then these pretreated samples were injected into a reversed-phase C(18) column with a gradient elution program, whereas acetonitrile-0.5% aqueous formic acid was used as mobile phase and detected by an on-line MS/MS system. As a result, the parent drug and its four metabolites were identified and characterized in rat urine for the first time by comparing their changes in molecular mass (ΔM), retention times and full-scan MS(n) spectra with those of the parent drug. A possible metabolic pathway of Polygalic acid was investigated and proposed.
CONCLUSIONS:
More importantly, the results demonstrated that the newly developed method (HPLC-ESI-MS(n)) was sensitive, simple and suitable for the determination of Polygalic acid and its metabolites in biological samples.