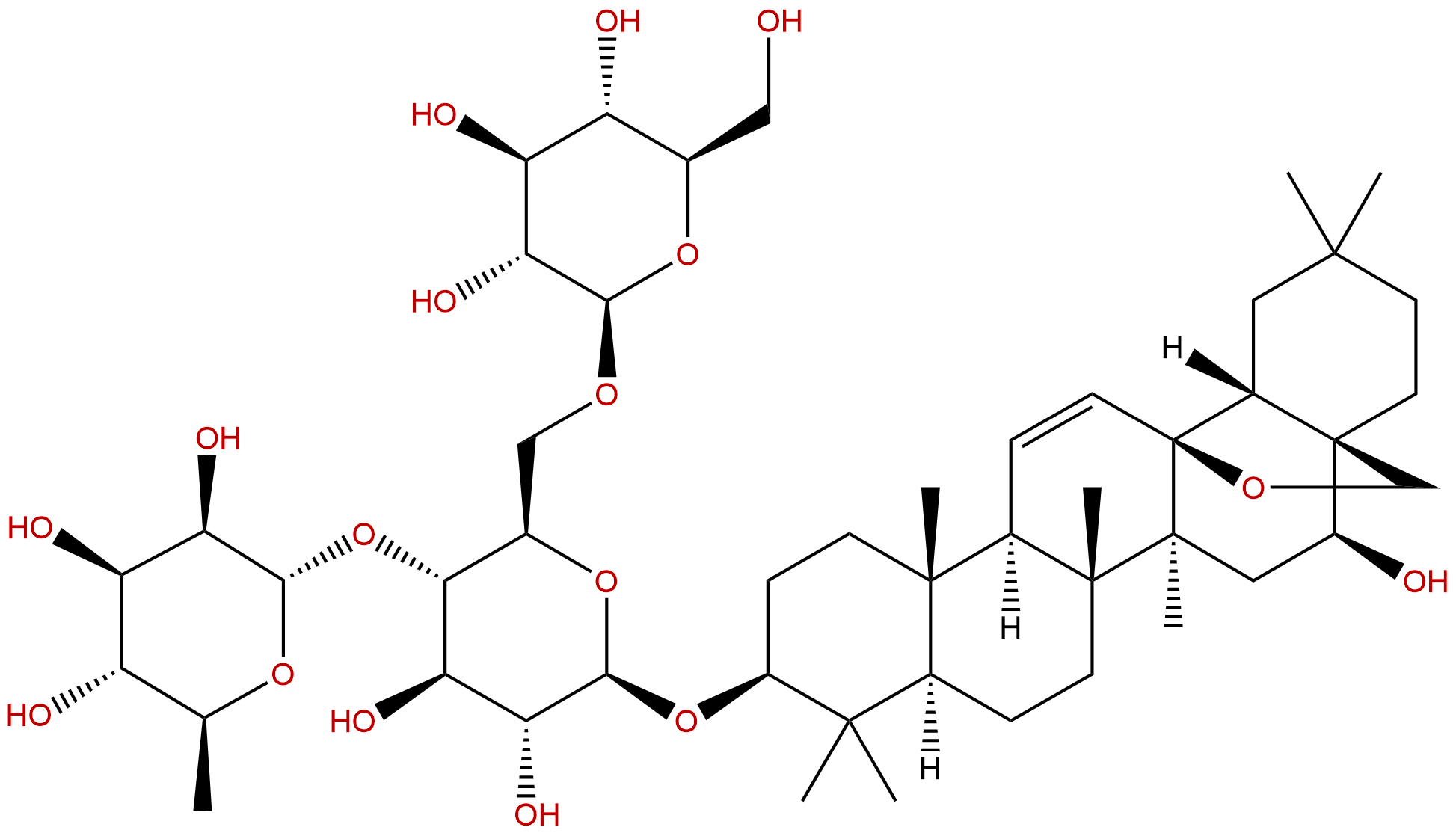
Saikosaponin CCAS No.:20736-08-7
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1241 |
| Formula: | C48H78O17 |
| Mol Weight: | 927.135 |
Product name: Saikosaponin C
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1241
Cas No.: 20736-08-7
Formula: C48H78O17
Mol Weight: 927.135
Botanical Source: Bupleurum falcatum
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Saikosaponin C (SSC) is one of the saikosaponins that are consisted in a Chinese herb, Radix Bupleuri, it yields a potent effect on inducing human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) viability and growth, also induces endothelial cells migration and capillary tube formation. [1]
Saikosaponin C can inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis by suppressing caspase-3 activation and subsequent degradation of focal adhesion kinase in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.[2]
Saikosaponin C seems to have beneficial effects on cellular tau function, it accelerates nerve growth factor (NGF)-mediated neurite outgrowth and increases the assembly of microtubules (MT) and synaptic marker proteins such as synaptophysin and PSD-95, suggests SSc might be a novel therapeutic tool for treating human AD and other neurodegenerative diseases. [3]
Saikosaponin C can cure liver disease.[4]
References:
[1] Shyu K G, Tsai S C, Wang B W, et al. Life Sci, 2004, 76(7):813-26.
[2] Lee T H, Chang J, Kim B M. Biochem Bioph Res Co, 2014, 445(3):615-21.
[3] Tae Ho Lee ?, Sung Ha Park ?, You M H, et al. J Neurochem, 2015, 136(6):1232-45.
[4] Chen Y C, Wang H M, Niu Q X, et al. Molecules, 2016, 21(2):153.
[5] Wang X D, Zhang Z W, Sun X M, et al. J Pharm Practice, 2001, 19(05):298-300.
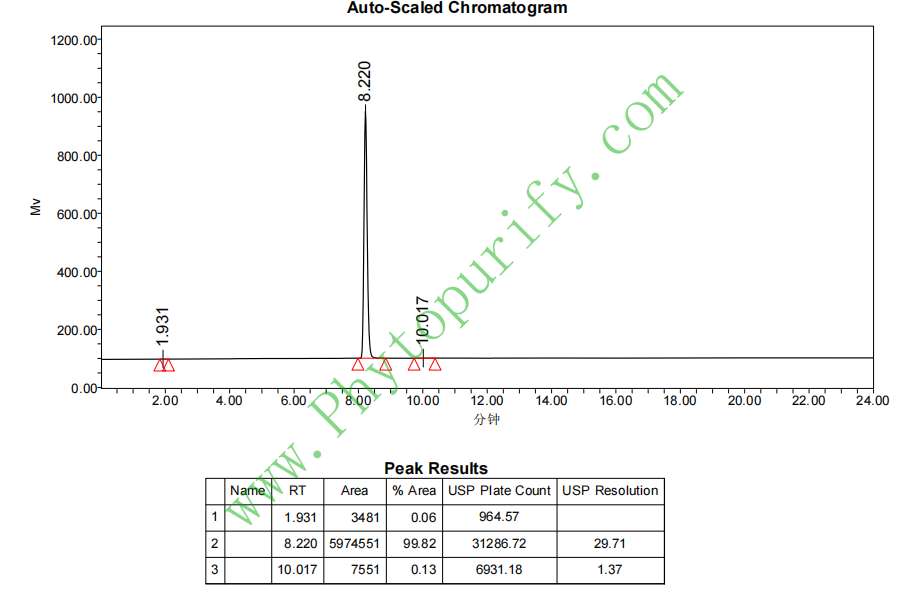
HPLC of Saikosaponin C