
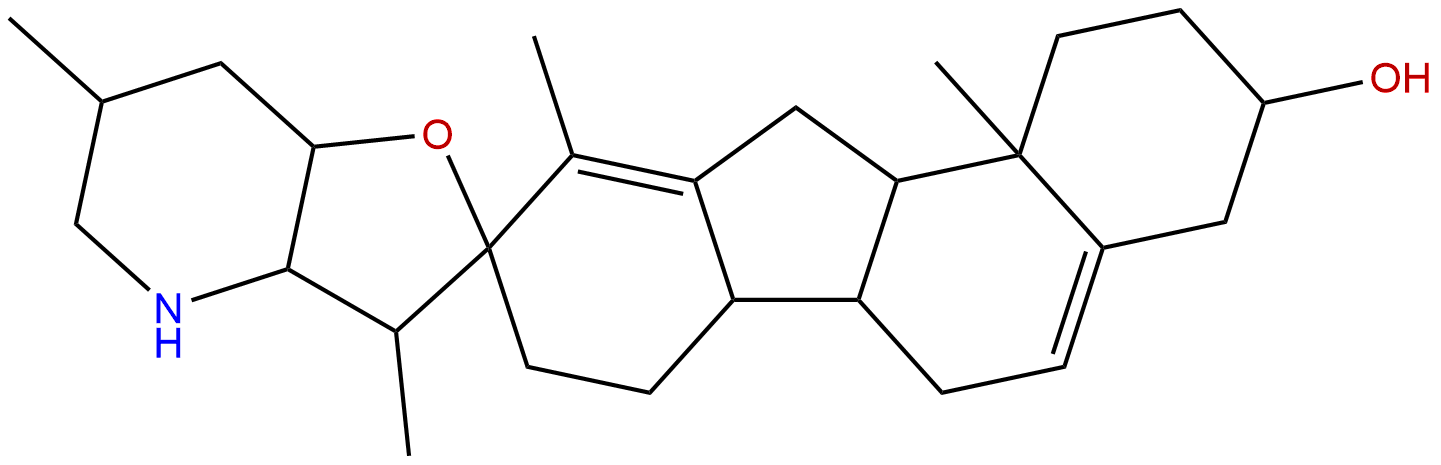
CyclopamineCAS No.:4449-51-8
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0437 |
| Formula: | C27H41NO2 |
| Mol Weight: | 411.63 |
Synonym name: Alkaloid V; 11-Deoxojervine
Catalogue No.: BP0437
Cas No.: 4449-51-8
Formula: C27H41NO2
Mol Weight: 411.63
Botanical Source: Veratrum californicum and Veratrum album (Liliaceae)
Purity: >99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to Kgs.
It can be produced in GMP plant on request.
Cyclopamine (11-deoxojervine) is a naturally occurring chemical that belongs to the group of steroidal jerveratrum alkaloids. It is a teratogen isolated from the corn lily (Veratrum californicum) that causes usually fatal birth defects. It can prevent the fetal brain from dividing into two lobes (holoprosencephaly) and cause the development of a single eye (cyclopia). Cyclopamine does so by inhibiting the hedgehog signaling pathway (Hh). Cyclopamine is useful in studying the role of Hh in normal development, and as a potential treatment for certain cancers in which Hh is overexpressed.
Cyclopamine was named for one-eyed lambs which were born to sheep which grazed on wild corn lily at a farm in Idaho. In 1957 the US Department of Agriculture started an eleven-year investigation which led to the identification of cyclopamine as the cause of the birth defect.
References