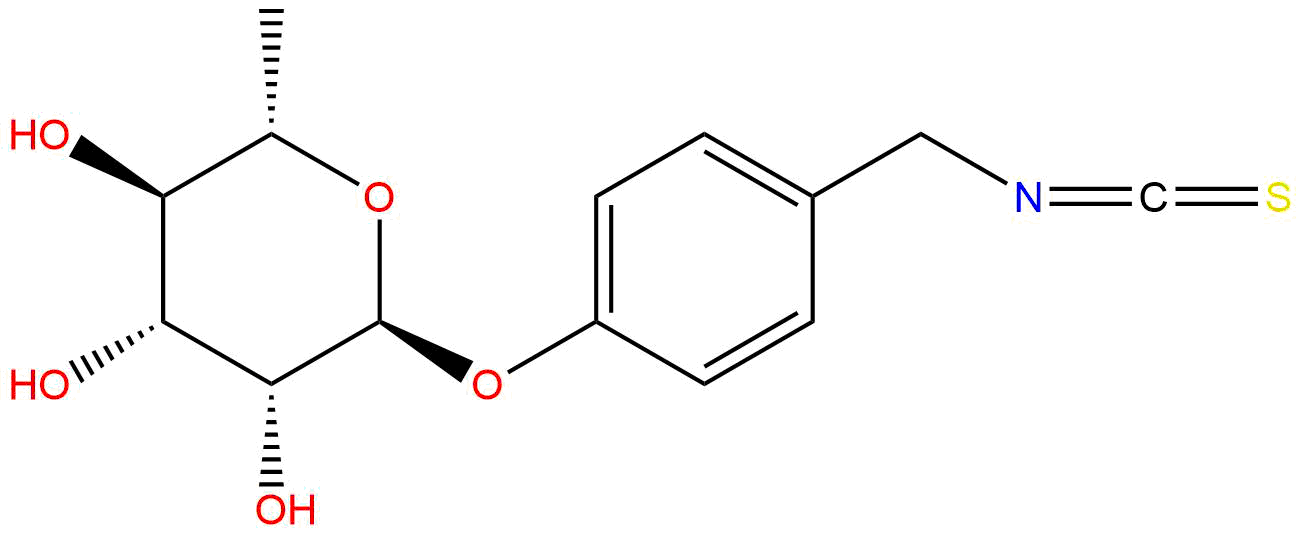
MoringinCAS No.:73255-40-0
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP4495 |
| Formula: | C14H17NO5S |
| Mol Weight: | 311.352 |
Product name: Moringin
Synonym name: 4-(α-L-Rhamnosyloxy)benzyl isothiocyanate
Catalogue No.: BP4495
Cas No.: 73255-40-0
Formula: C14H17NO5S
Mol Weight: 311.352
Botanical Source: Moringa Seeds
Type of Compound:
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
References:
Moringin and Its Structural Analogues as Slow H2S Donors: Their Mechanisms and Bioactivity
J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 27
Abstract
Moringin (rhamnobenzyl isothiocyanate) is a major bioactive compound in moringa seeds, which have been used as a healthy food. However, its bioactivity mechanisms are not well understood. We investigated moringin and its structurally similar analogues, including benzyl isothiocyanate and 4-hydroxylbenzyl isothiocyanate, for their hydrogen sulfide (H2S)-releasing activity triggered by cysteine. These isothiocyanates rapidly formed cysteine adducts, which underwent intramolecular cyclization followed by slowly releasing (a) organic amine and raphanusamic acid and (b) H2S and 2-carbylamino-4,5-dihydrothiazole-4-carboxylic acids. The product distributions are highly dependent on para-substituents on the phenyl group. Moringin has higher cytotoxicity to cancer cells and is a more potent anti-inflammatory agent than benzyl and hydroxybenzyl analogues, while benzyl isothiocyanate is a better antibacterial agent. Taken together, their bioactivity may not be directly related to their H2S donation activity. However, other metabolites alone do not have cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory activity. These findings indicated that their activity may be the combination effects of different metabolites via competitive pathways as well the para-substituent groups of benzyl ITCs.
Moringin, A Stable Isothiocyanate from Moringa oleifera, Activates the Somatosensory and Pain Receptor TRPA1 Channel In Vitro
Molecules February 2020 25(4):976
Abstract
Moringa oleifera Lam. is a tropical plant widely used in traditional medicines and as a food supplement. It is characterized by the presence of glucosinolates and isothiocyanates; the stable isothiocyanate 4-[(α-l-rhamnosyloxy)benzyl]isothiocyanate (moringin) has been widely studied for its bioactivity as hypoglycemic, antimicrobial, anticancer and in particular for its involvement in nociception and neurogenic pain. Moringa extracts and pure moringin were submitted to in vitro assays with the somatosensory TRPA1 ion channel, proving that moringin is a potent and effective agonist of this receptor involved in nociceptive function and pain states. Moringin do not activate or activates very weakly the vanilloids somatosensory channels TRPV1,2,3 and 4, and the melastatin cooling receptor TRPM8. The comparison of moringin’s activity with other known agonists of natural origin is also discussed.
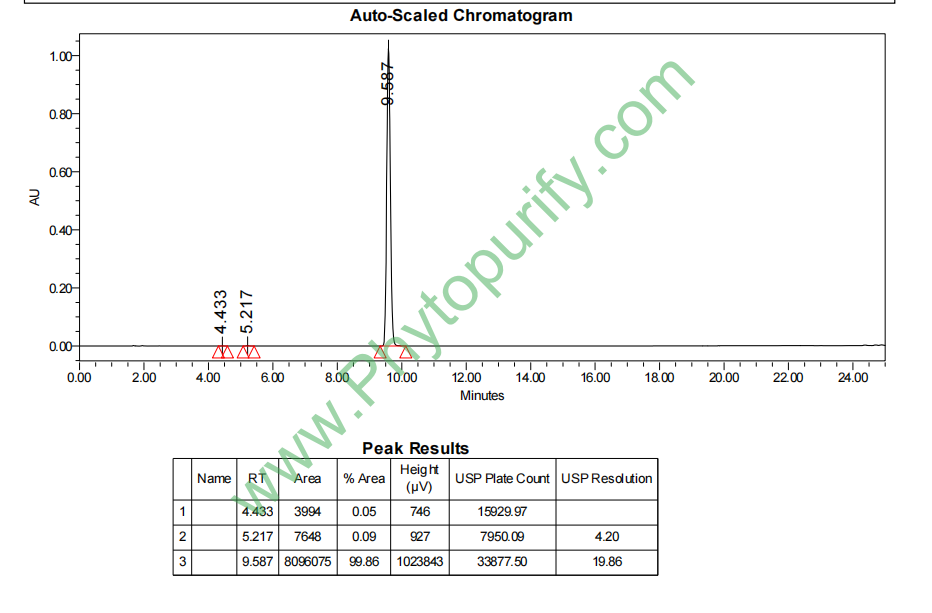
HPLC of Moringin