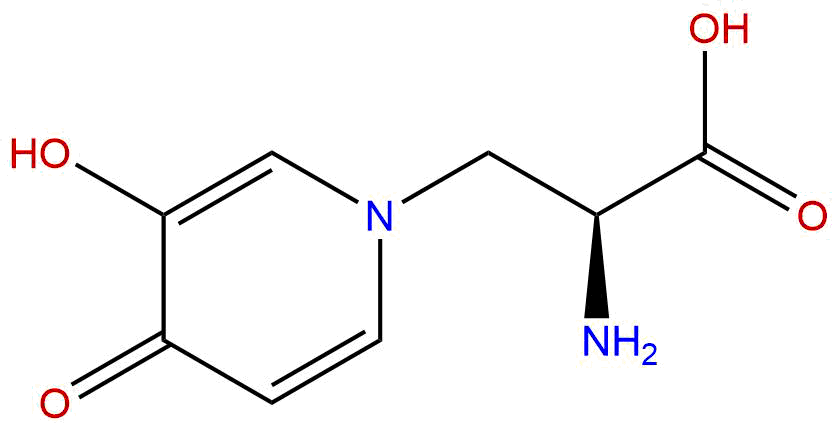
MimosineCAS No.:500-44-7
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
||||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP4806 |
| Formula: | C8H10N2O4 |
| Mol Weight: | 198.178 |
Product name: Mimosine
Synonym name: L-Mimosine
Catalogue No.: BP4806
Cas No.: 500-44-7
Formula: C8H10N2O4
Mol Weight: 198.178
Botanical Source:
Type of Compound: Alkaloids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, upto kilograms.
Inquire for bulk scale.
References:
1, J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 2959−2967
Abstract:
Mimosine is a nonprotein amino acid derived from plants known for its ability to bind to divalent and trivalent metal cations such as Zn2+, Ni2+, Fe2+, or Al3+. This results in interesting antimicrobial and anticancer properties, which make mimosine a promising candidate for therapeutic applications. One possibility is to incorporate mimosine into synthetic short peptide drugs. However, how this amino acid affects the peptide structure is not well understood, reducing our ability to design effective therapeutic compounds. In this work, we used computer simulations to understand this question. We first built parameters for the mimosine residue to be used in combination with two classical force fields of the Amber family. Then, we used atomistic molecular dynamics simulations with the resulting parameter sets to evaluate the influence of mimosine in the structural propensities for this amino acid. We compared the results of these simulations with homologous peptides, where mimosine is replaced by either phenylalanine or tyrosine. We found that the strong dipole in mimosine induces a preference for conformations where the amino acid rings are stacked over more extended conformations. We validated our results using quantum mechanical calculations, which provide a robust foundation for the outcome of our classical simulations.
2, https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01055
Pharmacodynamics
Mimosine inhibits DNA synthesis at the level of elongation of nascent chains by altering deoxyribonucleotide metabolism. It arrests the cell cycle in the late G(1) phase.
Mechanism of action
Mimosine causes inhibition of DNA replication, changes in the progression of the cells in the cell cycle, and apoptosis. Mimosine appears to introduce breaks into DNA. Mimosine is an iron/zinc chelator. Iron depletion induces DNA double-strand breaks in treated cells, and activates a DNA damage response that results in focal phosphorylation of histones. This leads to inhibition of DNA replication and/or DNA elongation. Some studies indicate that mimosine prevents the initiation of DNA replication, whereas other studies indicate that mimosine disrupts elongation of the replication fork by impairing deoxyribonucleotide synthesis by inhibiting the activity of the iron-dependent enzyme ribonucleotide reductase and the transcription of the cytoplasmic serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene (SHMT). Inhibition of serine hydroxymethyltransferase is moderated by a zinc responsive unit located in front of the SHMT gene.
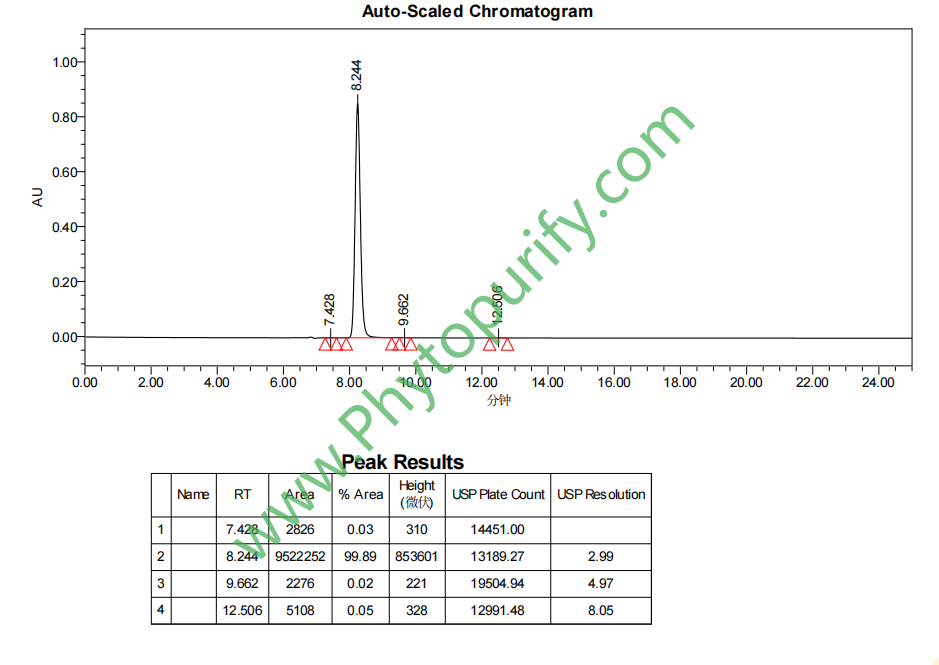
HPLC of Mimosine