
Nitidine ChlorideCAS No.:13063-04-2
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0998 |
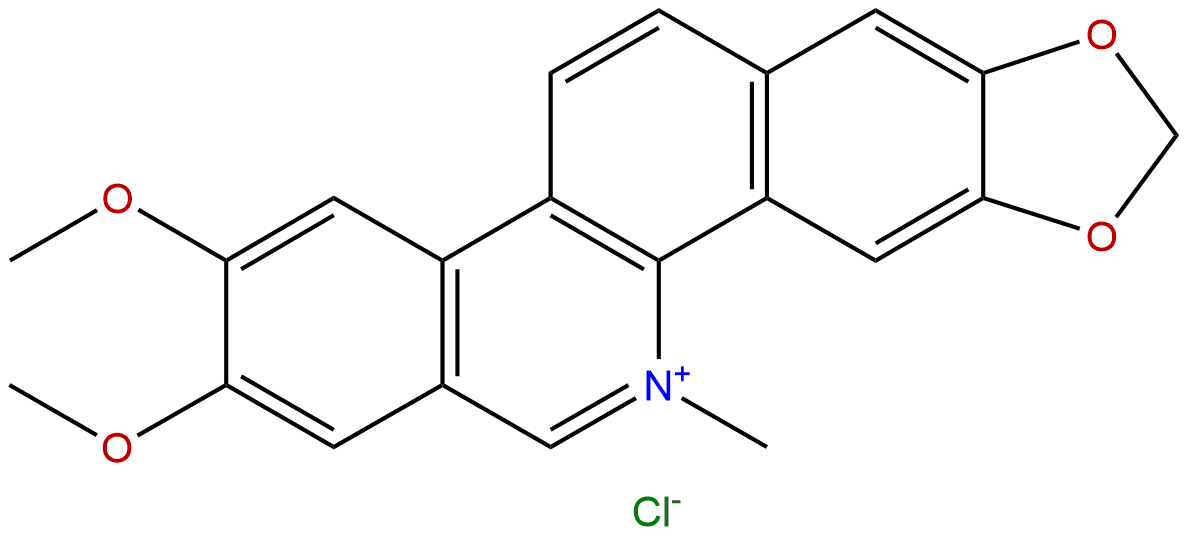
| Formula: | C21H18ClNO4 |
| Mol Weight: | 383.828 |
Product name: Nitidine Chloride
Synonym name: Angolinine Chloride; 6872-57-7
Catalogue No.: BP0998
Cas No.: 13063-04-2
Formula: C21H18ClNO4
Mol Weight: 383.828
Botanical Source: Zanthoxylum nitidum(Roxb.)DC.
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Alkaloids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Nitidine chloride has protective effects on rats during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion, it also exerts an anti-inflammatory property by inhibiting TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 production in association with reduced NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. It has inhibitory effects on various tumors, such as renal cancer , breast cancer.
References:
J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Oct 31;144(1):145-50.
Nitidine chloride inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines production via MAPK and NF-kappaB pathway in RAW 264.7 cells.
Zanthoxylum nitidium (Roxb.) DC. has long been used as a traditional herbal medicine for inflammatory diseases such as rheumatic arthritis and peridentitis. However, the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Nitidine chloride has not been fully elucidated. To determine the anti-inflammatory effects and mechanism of Nitidine chloride (NTD), a pentacyclic alkaloid is isolated from the root of Z. nitidium, in murine macrophages.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Anti-inflammatory properties of NTD were investigated using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated Raw 264.7 macrophages as in vitro model. The pro-inflammatory cytokines were evaluated by real-time RT-PCR and ELISA. Furthermore, intracellular signaling pathways were analyzed by Western blot and Immunofluorescence staining using specific antibodies. NTD significantly reduced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and IL-6 in both RNA and protein level. Moreover, transcriptional activity of NF-кB as well as the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 was significantly inhibited by NTD in a dose dependent manner. These results suggested that NTD exerts an anti-inflammatory property by inhibiting TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 production in association with reduced NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggested that NTD exerts an anti-inflammatory property by inhibiting TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 production in association with reduced NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. Nitidine chloride inhibits LPS-induced TNF alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 production via the suppression of phosphorylation of MAPK and the translocation of p65. In addition, these results revealed a novel role of NTD in regulation of inflammatory diseases.
Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Oct;60:246-51.
Nitidine chloride inhibits renal cancer cell metastasis via suppressing AKT signaling pathway.
Nitidine chloride (NC) has been shown to have anti-cancer effects on various tumors. However, whether NC could exert anti-metastasis activity in renal cancer cells and the underlying mechanisms have not been elucidated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, our data demonstrated the anti-metastasis effects of NC on renal cancer cells in vitro. With scratch assay and transwell assays, we found that NC potently suppressed the migration and invasion of 786-O and A498 cells. Mechanistically, we presented that NC significantly decreased phosphorylation of AKT, accompanied by down-regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Furthermore, a specific AKT inhibitor, LY294002, could enhance the anti-metastasis effects of NC, which indicated that NC suppressed metastasis of renal cancer cells partly via inhibition of AKT activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our results imply that NC can be developed as a potential anti-metastasis agent to renal cancer.