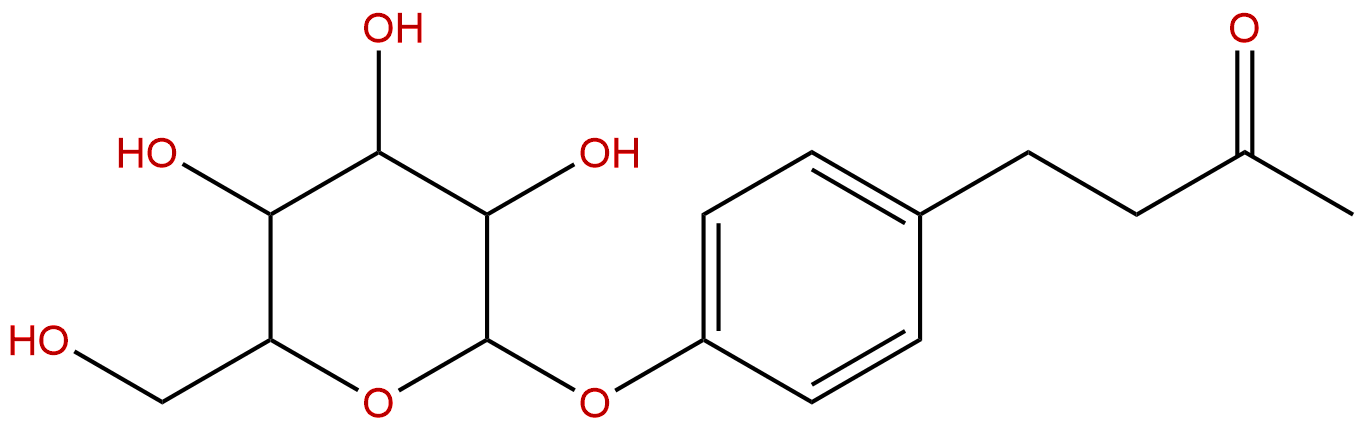
Raspberry ketone glucosideCAS No.:38963-94-9
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1197 |
| Formula: | C16H22O7 |
| Mol Weight: | 326.345 |
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1197
Cas No.: 38963-94-9
Formula: C16H22O7
Mol Weight: 326.345
Botanical Source: Artemisia santolinifolia, Pinus spp., Rheum spp. and raspberries
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Raspberry ketone glucoside has lasting effects for the inhibition of melanogenesis and various melanogenic factors after the degradation in the skin.
References:
Journal of Society of Cosmetic Chemists of Japan, 2001, 35(2):120-126.
Lasting Effect of Raspberry Ketone Glucoside on Whitening.
Tyrosinase is well-known as a key enzyme responsible for the production of melanin in melanocytes. It is also known that inflammatory reactions such as active oxygen species and melanogenic factors in the skin are induced by UV irradiation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The keys to suppress melanin synthesis are considered to be not only the inhibition of tyrosinase activity but also that of inflammatory reactions. Raspberryketone glucoside (RKG) in raspberry fruit (Rubus ideaeus) had the inhibitory effect on the melanin synthesis. As a result of an investigation with the glycosides that have similar structure of RKG at its glycoside moieties and alkyl chain, the structure of RKG was found to be suitable as an inhibitory factor on melanogenesis. RKG released raspberry ketone (RK) gradually after the reaction with both homogenated and desquamated cells of the stratum corneum. In addition to the inhibitory effect of melanin synthesis, RK also showed remarkable functions such as the scavenge of nitric oxide (NO) which was considered to induce pigmentation of human skin through activation of melanogenesis and the inhibition of the inflammation-related reactions such as production of superoxide anion and lipid peroxide.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data indicated that RKG had lasting effects for the inhibition of melanogenesis and various melanogenic factors after the degradation in the skin.
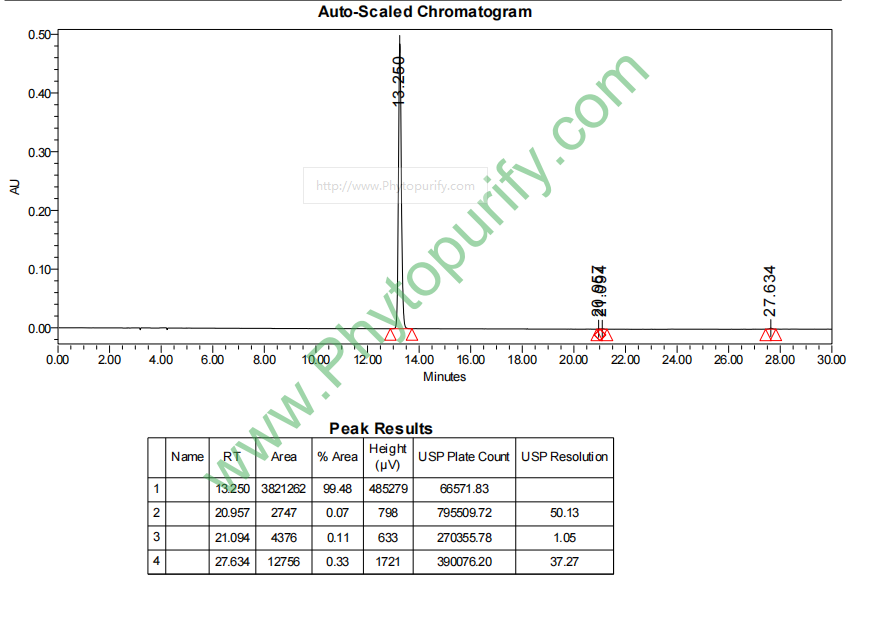
HPLC of Raspberry ketone glucoside