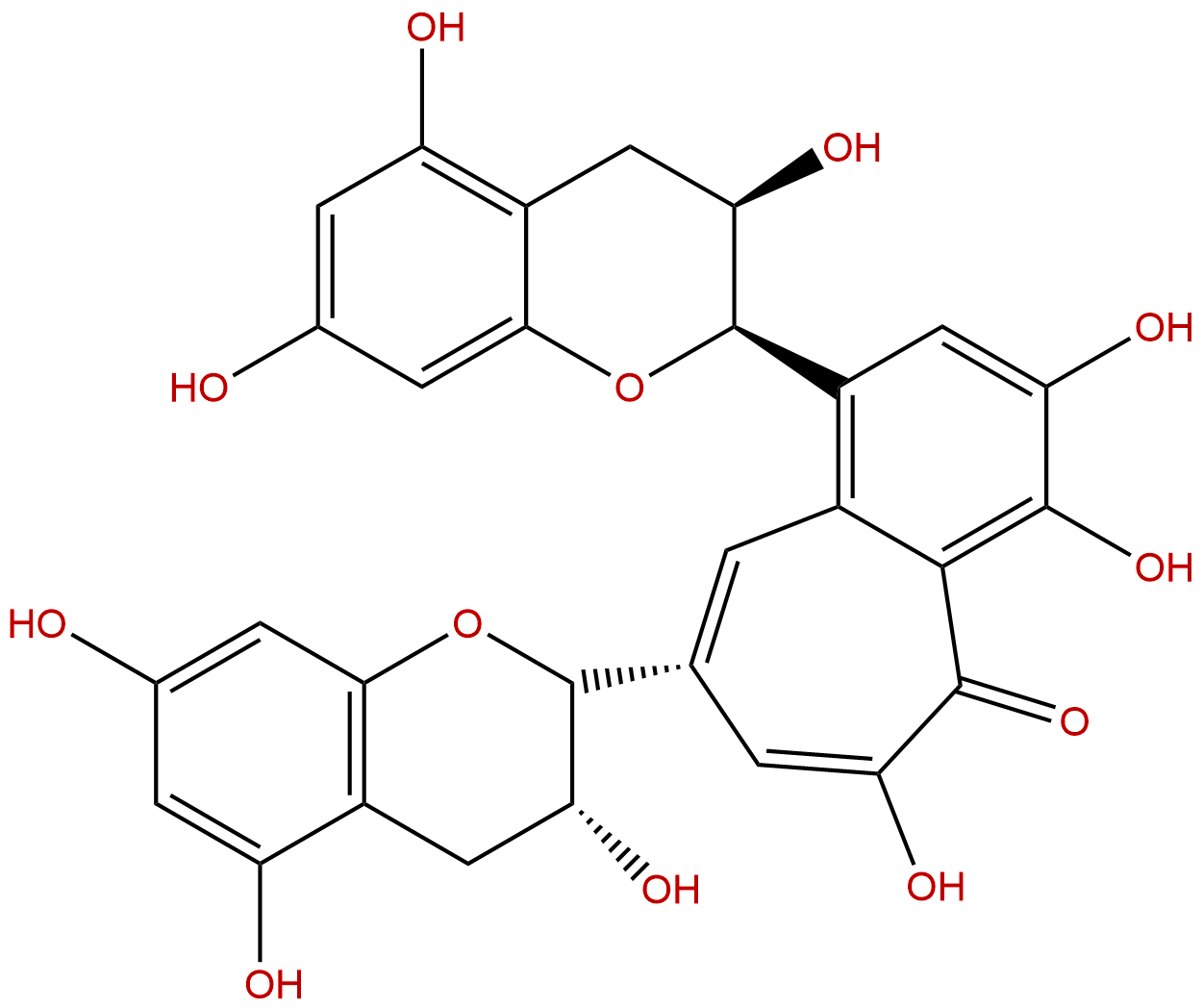
TheaflavinCAS No.:4670-05-7
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1384 |
| Formula: | C29H24O12 |
| Mol Weight: | 564.499 |
Product name: Theaflavin
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1384
Cas No.: 4670-05-7
Formula: C29H24O12
Mol Weight: 564.499
Botanical Source: black tea (Camellia sinensis)
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Polyphenols
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Theaflavins(TF) has antioxidant activity, the TF present in black tea possess at least the same antioxidant potency as catechins present in green tea, and that the conversion of catechins to TF during fermentation in making black tea does not alter significantly their free radical-scavenging activity.[1,2]
Theaflavins significantly reduce lipid accumulation, suppressed fatty acid synthesis, and stimulate fatty acid oxidation, also inhibits acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase activities by stimulating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) through the LKB1 and reactive oxygen species pathways; it is bioavailable both in vitro and in vivo and may be active in the prevention of fatty liver and obesity.[3]
Theaflavins induce G2/M arrest by modulating expression of p21 waf1/cip1 , cdc25C and cyclin B in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells, it acts as an effective anti-proliferative agent by modulating cell growth regulators in prostate cancer cells.[4]
Theaflavins from Black Tea, have inhibition of ultraviolet B&ndash and induces AP‐1 activation.[5]
Theaflavins inhibit 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK)-induced lung tumorigenesis in A/J mice.[6]
Theaflavins and thearubigins have antimutagenic effects in Ames Salmonella assays.[7]
References:
[1] Leung L K, Su Y, Chen R, et al. J Nut, 2001, 131(9):2248-51.
[2] Lin C L, Huang H C, Lin J K. J Lipid Res, 2007, 48(11):2334-43.
[3] Masaaki N, Ma W, Huang C, et al. Mol Carcinogen, 2000, 28:148-55.
[4] Prasad S, Kaur J, Roy P, et al. Life Sci, 2007, 81(17-18):1323-31.
[5] Yang G Y, Liu Z, Seril D N, et al. Carcinogenesis, 1997, 18(12):2361-5.
[7] Gupta S, Chaudhuri T, Seth P, et al. Phytother Res, 2002, 16(7):655-61.
[8] Kim S Y, Kozukue N, Han J S, et al. ?????????38??1?, 2006, 38(1):5-9.
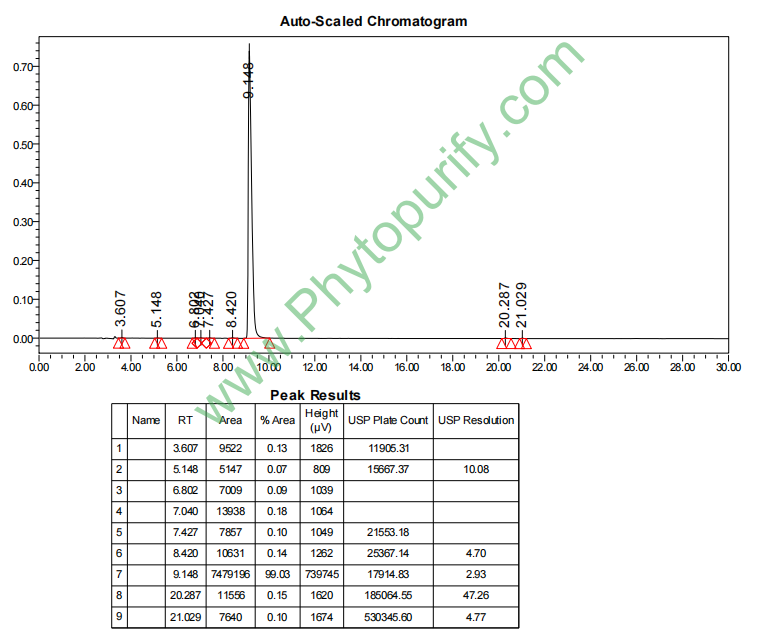
HPLC of Theaflavin
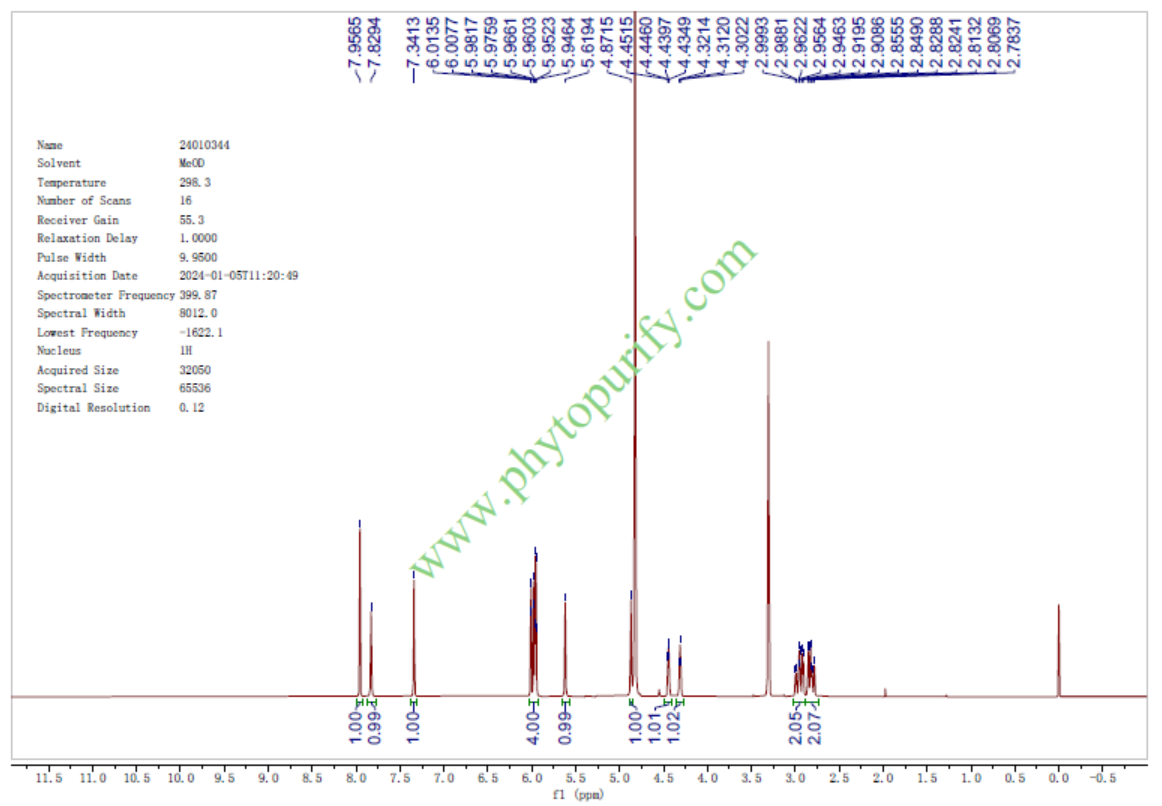
HNMR of Theaflavin