MiglustatCAS No.:72599-27-0
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
||||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP5229 |
| Formula: | C10H21NO4 |
| Mol Weight: | 219.281 |
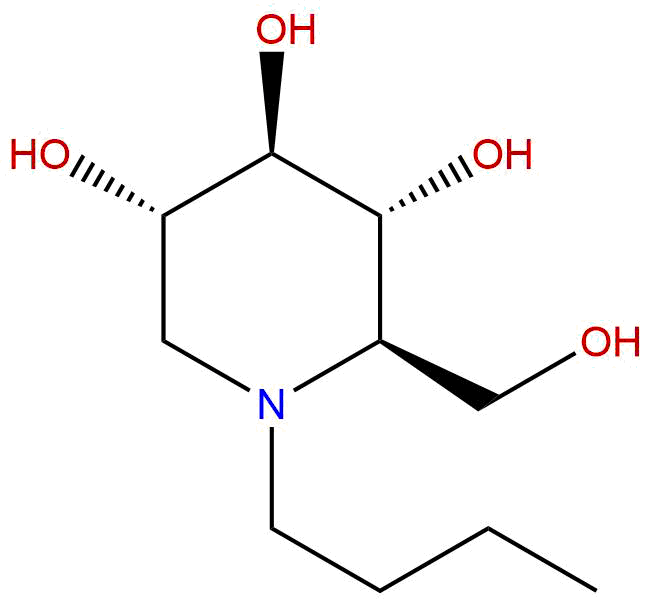
Product name: Miglustat
Synonym name: N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin
Catalogue No.: BP5229
Cas No.: 72599-27-0
Formula: C10H21NO4
Mol Weight: 219.281
Botanical Source:
Type of Compound: Alkaloids
Purity: 99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Miglustat, commonly marketed under the trade name Zavesca, is a drug used to treat Gaucher disease. It inhibits the enzyme glucosylceramide synthase, an essential enzyme for the synthesis of most glycosphingolipids. It is only used for patients who cannot be treated with enzyme replacement therapy with imiglucerase. Miglustat is now the first and only approved therapy for patients with Niemann-Pick disease type C (NP-C). It has recently been approved for treatment of progressive neurological symptoms in adult and pediatric patients in the European Union, Brazil, and South Korea.
Miglustat, an N-alkylated imino sugar, is a synthetic analogue of D-glucose. Miglustat is an inhibitor of the enzyme glucosylceramide synthase, which is a glucosyl transferase enzyme responsible for catalyzing the formation of glucosylceramide (glucocerebroside). Glucosylceramide is a substrate for the endogenous glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme that is deficient in Gaucher's disease. The accumulation of glucosylceramide due to the absence of glucocerebrosidase results in the storage of this material in the lysosomes of tissue macrophages, leading to widespread pathology due to infiltration of lipid-engorged macrophages in the viscera, lymph nodes, and bone marrow. This results in secondary hematologic consequences including sever anemia and thrombocytopenia, in addition to the characteristic progressive hepatosplenomegaly, as well as skeletal complications including osteonecrosis and osteopenia with secondary pathological fractures.
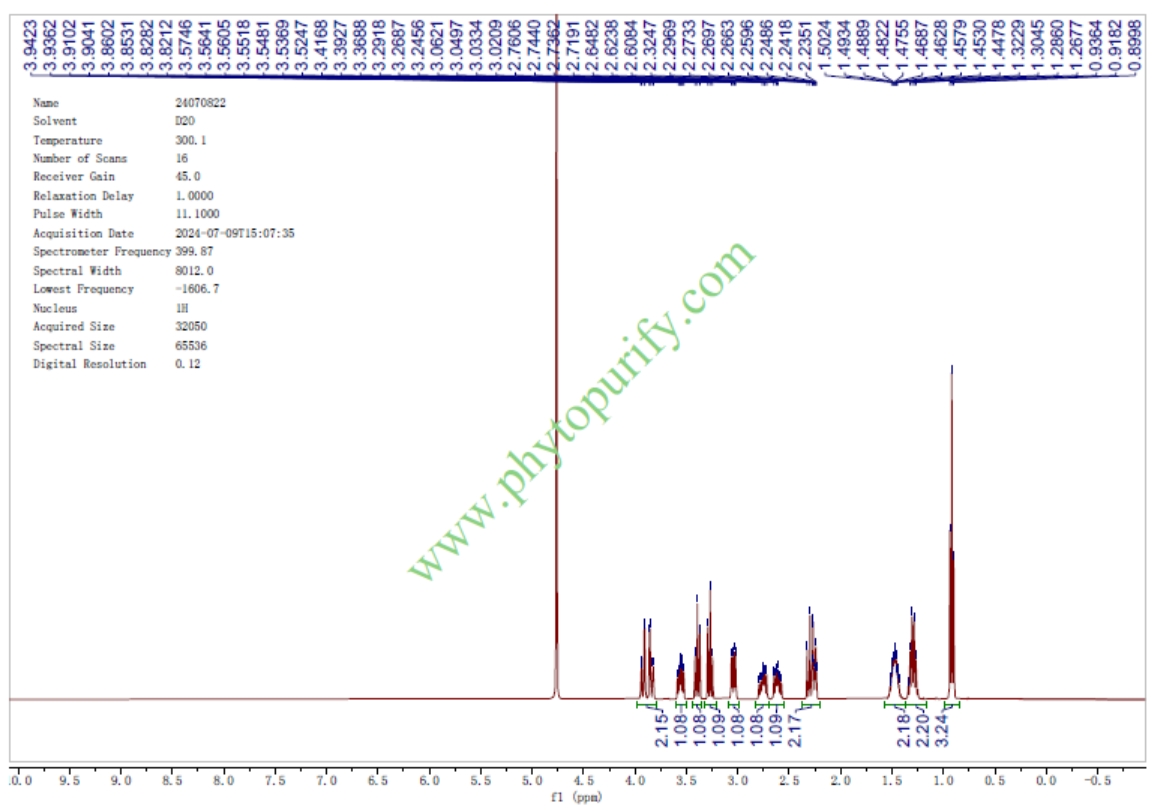
HPLC of Miglustat
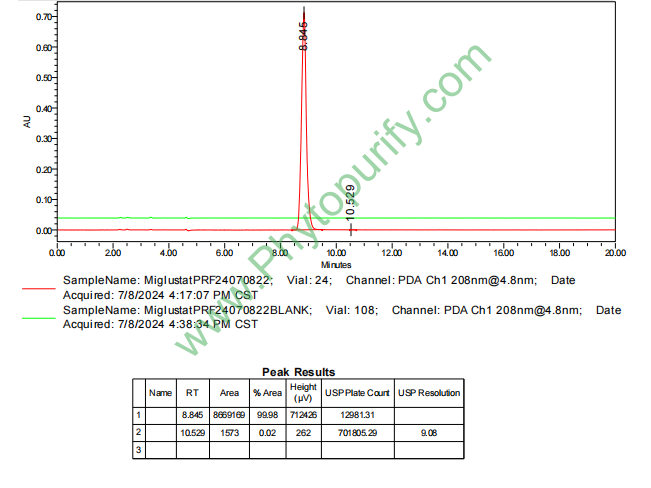
HNMR of Miglustat