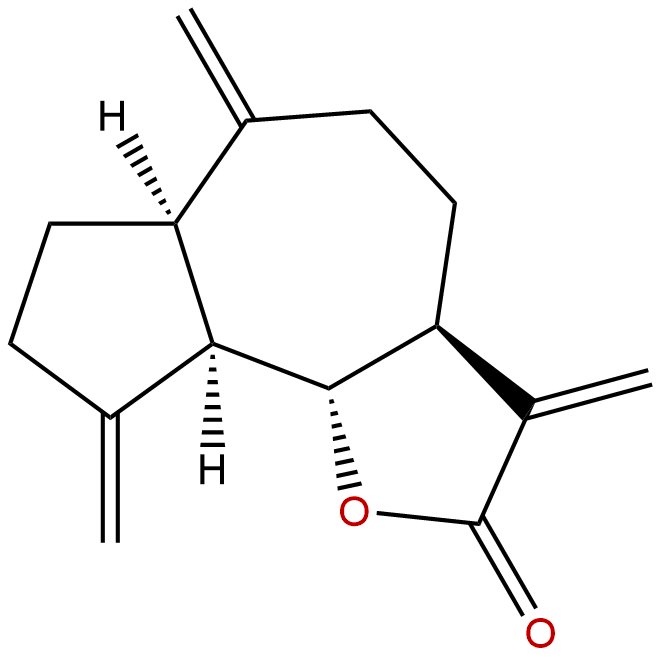
Dehydrocostus LactoneCAS No.:477-43-0
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0461 |
| Formula: | C15H18O2 |
| Mol Weight: | 230.307 |
Product name: Dehydrocostus Lactone
Synonym name: Epiligulyl oxide
Catalogue No.: BP0461
Cas No.: 477-43-0
Formula: C15H18O2
Mol Weight: 230.307
Botanical Source: Saussurea lappa, Veronica hirsuta and Zaluzania tribolia
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Sesquiterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Dehydrocostus lactone(DCL) is exuded from sunflower roots and low DCL concentrations stimulate germination of the root parasite Orobanche cumana.[1]
Dehydrocostus lactone(0.1-10microg/ml) can protect osteoblasts against H(2)O(2)
-induced cellular dysfunction, may be valuable as a protective agent against oxidative damage in osteoblasts.[2]
Dehydrocostus lactone increases cellular resistance to oxidant injury in HepG2 cells, may via causing the nuclear accumulation of the nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and increasing the promoter activity of antioxidant response element (ARE).[3]
Dehydrocostus lactone and costunolide exhibits strong larvicidal activity against A. albopictus with LC(50) values of 2.34 and 3.26 ug/ml, respectively, while the essential oil had an LC(50) value of 12.41 ug/ml. [4]
References:
[1] El-Nadi M, Zohni O. Phytochemistry, 2011, 72(7):624-34.
[2] Choi E M, Kim G H, Yong S L. Toxicol In Vitro, 2009, 23(5):862-7.
[3] Jeong G S, Pae H O, Jeong S O, et al. Eur J Phamarmacol, 2007, 565(565):37-44.
[4] Zhi L L, He Q, Sha S C, et al. Parasitol Res?, 2011, 110(6):2125-30.
[5] Tan S J, Qiu D, Liu G, et al. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2011, 31(1):145-7.
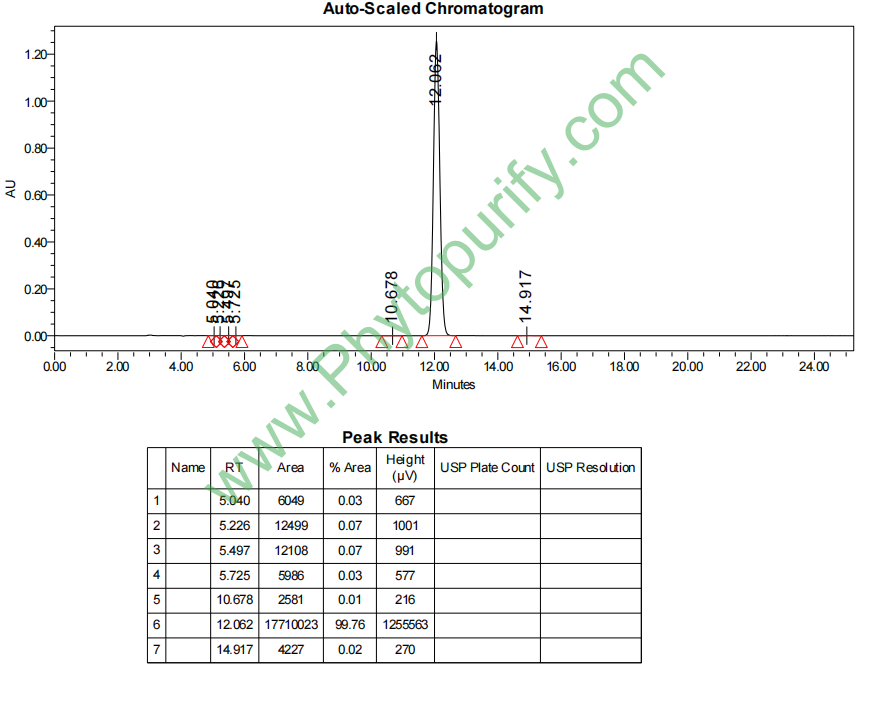
HPLC of Dehydrocostus Lactone
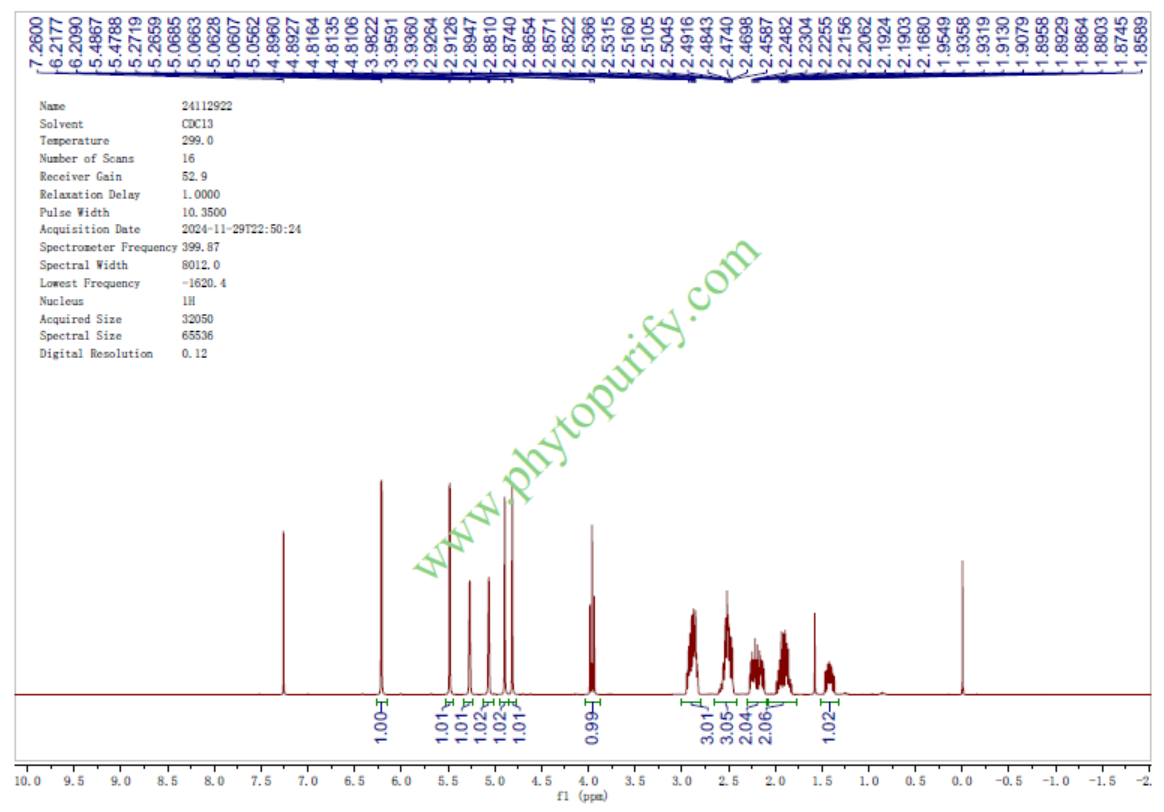
HNMR of Dehydrocostus Lactone