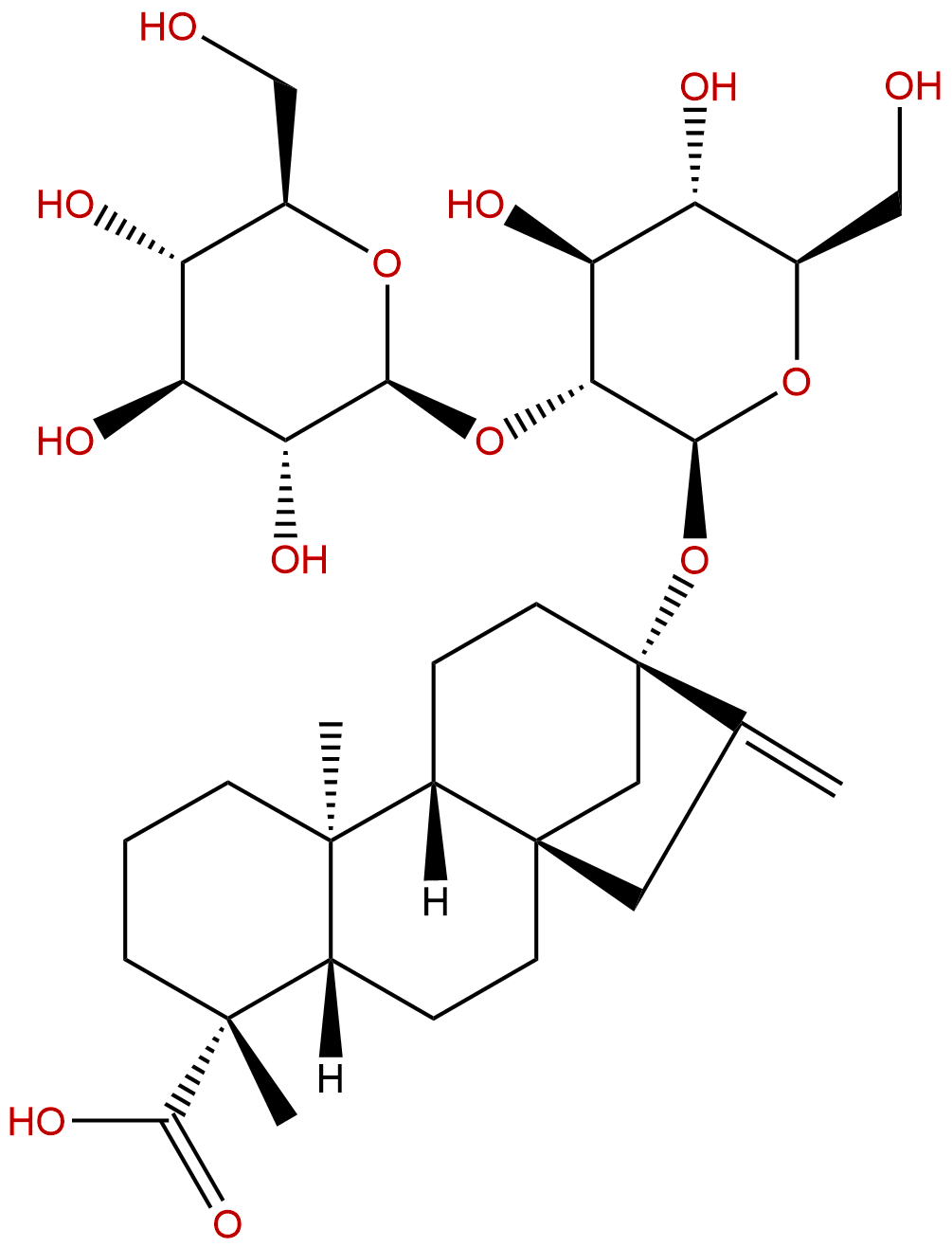
steviolbiosideCAS No.:41093-60-1
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1501 |
| Formula: | C32H50O13 |
| Mol Weight: | 642.739 |
Product name: steviolbioside
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1501
Cas No.: 41093-60-1
Formula: C32H50O13
Mol Weight: 642.739
Botanical Source: Stevia rebaudiana (stevia)
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Diterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
We provide solution to improve the water-solubility of compounds, thereby facilitating the variety of activity tests and clinic uses.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Steviolbioside is a natural sweetener, it presents notable inhibition on human hepatocarcinoma cell Hep3B, human breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 and human pancreatic cancer cell BxPC-3, thus, steviolbioside could be a potential remedy for human breast cancer. Steviolbioside also exhibits moderate antituberculosis activity against M. tuberculosis strain H37RV in vitro.
References:
Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 2011, 46(6):902-5.
Antituberculosis activity of glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana and hybrid compounds of steviolbioside and pyridinecarboxylic acid hydrazides
Stevioside and Steviolbioside, glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni, in addition to hybrid compounds synthesized from Steviolbioside and the antituberculosis drug isoniazid and its isomer nicotinic acid hydrazide exhibited moderate antituberculosis activity against M. tuberculosis strain H37RV in vitro (MIC = 7.5, 3.75, 5, and 10 μg/mL, respectively).
Food Chem. 2016 Apr 1;196:155-60.
Production of a bioactive sweetener steviolbioside via specific hydrolyzing ester linkage of stevioside with a β-galactosidase.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A β-galactosidase from Kluyveromyces lactis was found to specifically catalyze hydrolysis of the glycosyl ester linkage of stevioside to yield Steviolbioside, a rare sweetener that also exists in Stevia rebaudiana leaves. In a packed bed reactor, a reaction coupling separation was realized and a production yield of Steviolbioside reached 90% in 6 h. The hydrolysis product Steviolbiosidepresented higher cytoxicity on human normal cells (hepatocytes cell L02 and intestinal epithelial cell T84) than stevioside did. Comparing to the typical chemotherapy agent, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), Steviolbioside presents much lower cytotoxicity on all assayed human normal cells; it presented notable inhibition on human hepatocarcinoma cell Hep3B, human breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 and human pancreatic cancer cell BxPC-3.
CONCLUSIONS:
The remarkable inhibition on MDA-MB-231 cells makes Steviolbioside a potential remedy for human breast cancer, when Steviolbioside is served as a natural sweetener.
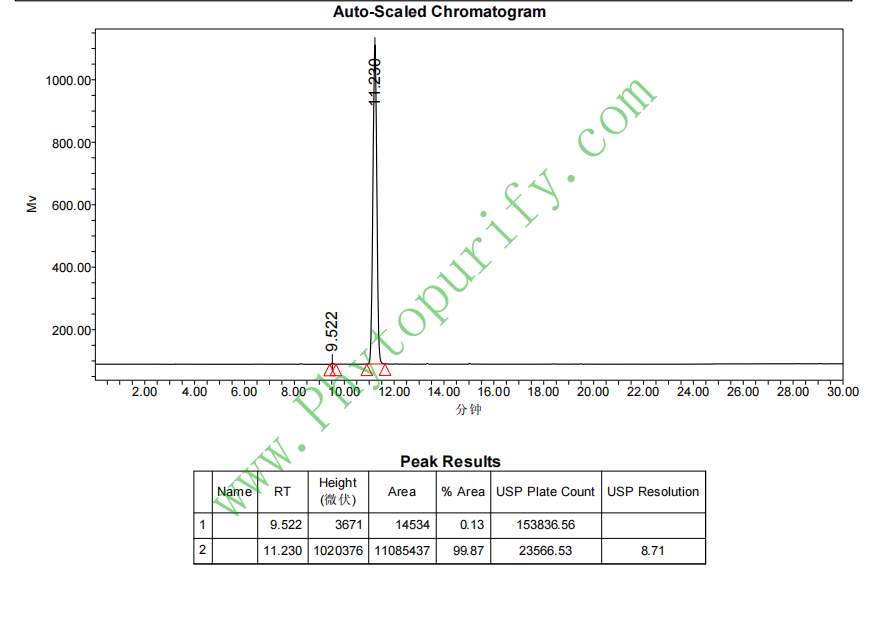
HPLC of steviolbioside
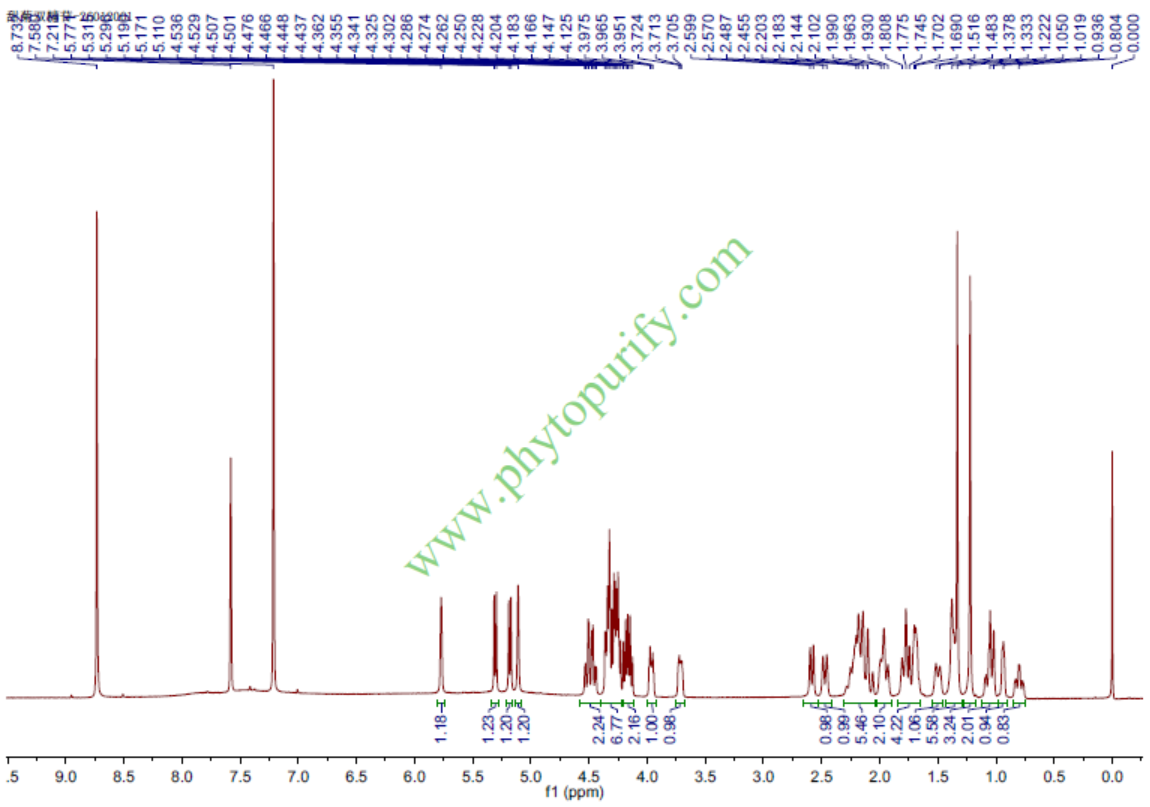
HNMR of steviolbioside