Ginkgolide JCAS No.:107438-79-9 |
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0649 |
| Formula: | C20H24O10 |
| Mol Weight: | 424.402 |
| Botanical Source: | Ginkgo biloba L. |
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP0649
Cas No.: 107438-79-9
Formula: C20H24O10
Mol Weight: 424.402
Botanical Source: Ginkgo biloba (ginkgo)
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Ginkgolide J has neuroprotective activity, it can prevent A beta(1-42) induced inhibition of long-term potentiation in the CA1 region of mouse hippocampal slices, it is also capable of inhibiting cell death of rodent hippocampal neurons caused by A beta(1-42). Ginkgolide J can inhibit platelet aggregation induced by ADP or PAF.
References:
Neurobiol Aging. 2009 Feb;30(2):257-65. Epub 2007 Jul 20.
Protection against beta-amyloid induced abnormal synaptic function and cell death by Ginkgolide J.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A new Ginkgo biloba extract P8A (TTL), 70% enriched with terpene trilactones, prevents A beta(1-42) induced inhibition of long-term potentiation in the CA1 region of mouse hippocampal slices. This neuroprotective effect is attributed in large part to Ginkgolide J that completely replicates the effect of the extract. Ginkgolide J is also capable of inhibiting cell death of rodent hippocampal neurons caused by A beta(1-42).
CONCLUSIONS:
This beneficial and multi-faceted mode of action of the ginkgolide makes it a new and promising lead in designing therapies against Alzheimer's disease.
Chem Biol Interact. 1997 Oct 24;106(3):183-90.
Antioxidative activity of ginkgolides against superoxide in an aprotic environment.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The terpene lactones ginkgolide A, ginkgolide B, ginkgolide C, Ginkgolide J and bilobalide, which are components of a standardized extract (EGb 761) from leaves of Ginkgo biloba, as well as ginkgolide M from roots of G. biloba were studied regarding their reaction against superoxide (O2-) and hydroperoxyl radicals (HO2) in dimethyl sulfoxide as an aprotic solvent. It was found that the ginkgolides B, C, J, M as well as bilobalide react with superoxide and its protonated form as demonstrated by EPR and UV/VIS spectroscopy. The initial reaction rate with these oxygen-derived radicals is in the order of 100 M-1/s and below. Ginkgolide A does not react with superoxide under these conditions.
CONCLUSIONS:
From these findings it can be suggested that the superoxide scavenging effect of the ginkgolides B, C, J, M and bilobalide contributes to the antioxidant properties of G. biloba.
Exp Brain Res. 2007 Jun;179(4):665-71.
Ginkgolides protect primary cortical neurons from potassium cyanide-induced hypoxic injury.
In this study, we investigated the effects of ginkgolides (ginkgolide A, ginkgolide B, ginkgolide C and Ginkgolide J), the main constituent of the non-flavone fraction of EGb 761, on hypoxic injury induced by potassium cyanide (KCN) in primary cortical neurons.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The neurons were pretreated with or without ginkgolides for 24 h before incubation with KCN for 4 h. The results demonstrated that KCN (0.05 mmol/l) significantly decreased cell viability and increased LDH release (P < 0.05 versus the control). The characteristic changes of neuronal morphology induced by KCN were observed. However, pretreatment of neurons with 37.5 microg/ml of ginkgolides (ginkgolides + KCN group) led to a significant increase in cell viability, a decrease in LDH release (P < 0.05 versus the KCN group) and a remarkable improvement in cellular morphology in hypoxic neurons compared with the KCN group.
CONCLUSIONS:
The data suggested that ginkgolides have a significant role to protect the primary cortical neurons from hypoxic injury induced by KCN.
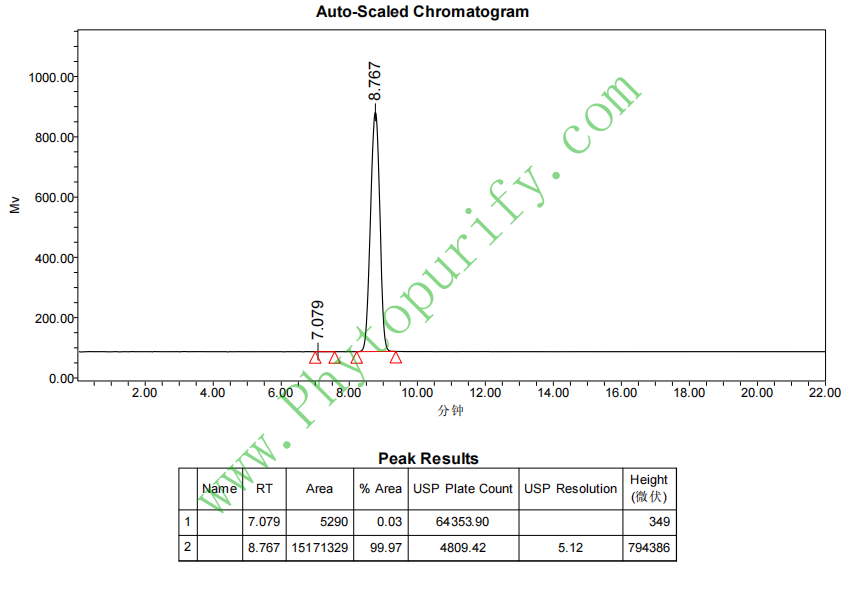
HPLC of Ginkgolide J