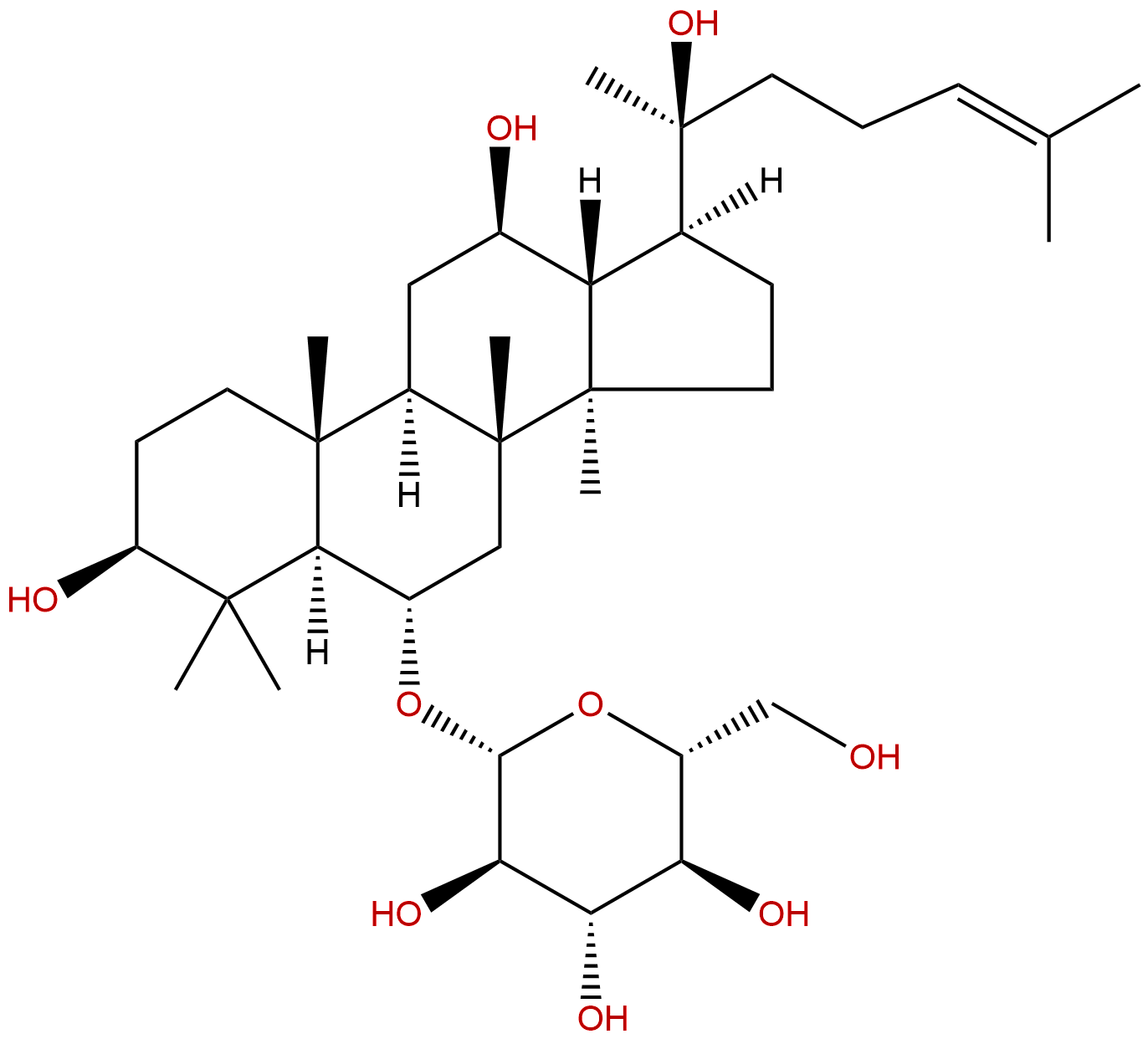
Ginsenoside Rh1CAS No.:63223-86-9
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0667 |
| Formula: | C36H62O9 |
| Mol Weight: | 638.883 |
Product name: Ginsenoside Rh1
Synonym name: Sanchinoside B2
Catalogue No.: BP0667
Cas No.: 63223-86-9
Formula: C36H62O9
Mol Weight: 638.883
Botanical Source: Panax spp.
Physical Description: White powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Ginsenoside Rh1 has antiallergic action , may originate from its cell membrane-stabilizing and anti-inflammatory activities, and can improve the inflammation caused by allergies.[1]
Ginsenoside Rh1 (2065mg/kg, oral ) suppresseS body and epididymal fat weight gains and plasma triglyceride level in DIO mice, also inhibits the expressions of PPAR-γ, C/EBP-α, fatty acid synthase, adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein, as well as F4/80, CD68, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β in DIO mice by real time PCR analysis, suggests it may ameliorate obesity, by inhibiting adipocyte differentiation and inflammation.[2]
Ginsenoside Rh1 can upregulate glucocorticoid receptor (GR) level, suggests Rh1 may improve glucocorticoid efficacy in hormone-dependent diseases, it may enhance the effect of Dex in the treatment of MRL/lpr mice through regulating CD4+ T cells activation and Th1/Th2 balance.[3]
Ginsenoside Rh1 can inhibit MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways and downstream transcription factors such as NF-κB and AP-1, which play an important role in MMP gene expressions, suggests that ginsenoside Rh1 may have a therapeutic potential for malignant gliomas.[4]
Ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits IFN-gamma-induced JAK/STAT and ERK signaling pathways and downstream transcription factors, and thereby iNOS gene expression, thus, the inhibition of microglial activation by ginsenoside Rh1 may provide potential therapeutic strategy for various neuroinflammatory diseases.[5]
Ginsenoside Rh1(Rh1) has been reported to possess antiallergic and anti-inflammatory activities, treatment of Rh1 can decrease the levels of MCP-1 and CCR2 and the expression of VLA5 and activated β1 integrin on the cell surface, and attenuate the phosphorylation of MAPKs, the inhibitory effects of Rh1 on monocyte function should be regarded as a promising new anti-inflammatory response with a potential therapeutic role against inflammation-dependent diseases.[6]
References:
[1] Park E K, Choo M K, Han M J, et al. Int Arch Allergy Immu, 2004, 133(2):113-20.
[2] Gu W, Kim K A, Kim D H. Biol Pharm Bull, 2013, 36(1):102-7.
[3] Feng Y, Wang C, Cheng S, et al. Evid-based Compl Alt , 2014, 2015:1-8.
[4] Jung J S, Ahn J H, Le T K, et al. Neurochem Int, 2013, 63(2):80-6.
[5] Jung J S, Kim DHKim H S. Biochem Bioph Res Co, 2010, 397(2):323-8.
[6] Choi Y J, Yoon J H, Cha S W, et al. Fitoterapia, 2011, 82(6):911-9.
[7] Zheng‐Liang Ye, Chu‐Chu Hu, Xiao‐Hui Fan, et al. J Liq Chromatogr R T, 2005, 29(11):1575-87.
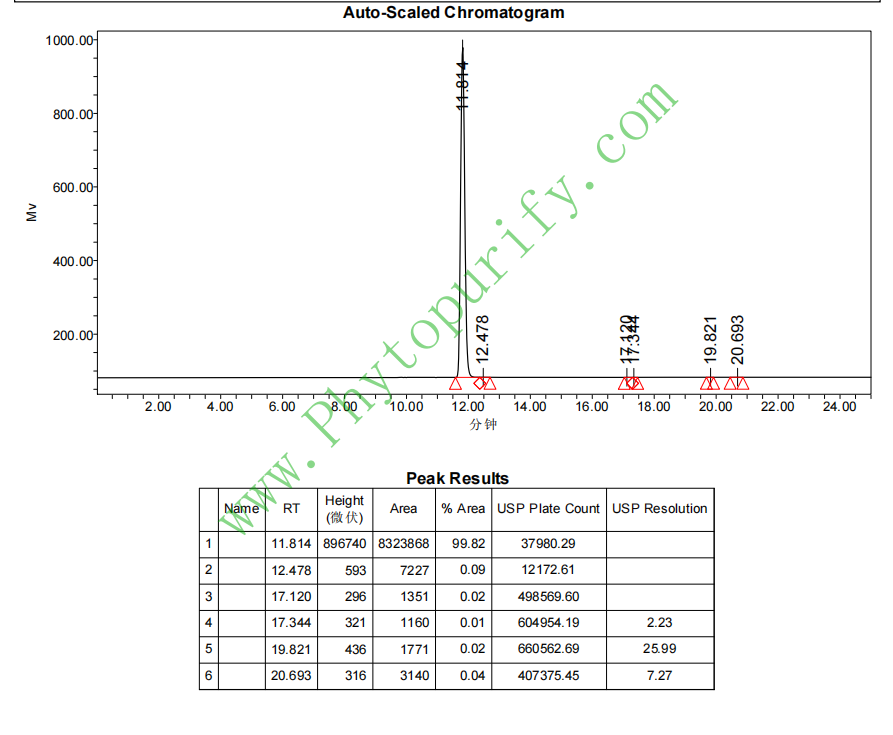
HPLC of Ginsenoside Rh1
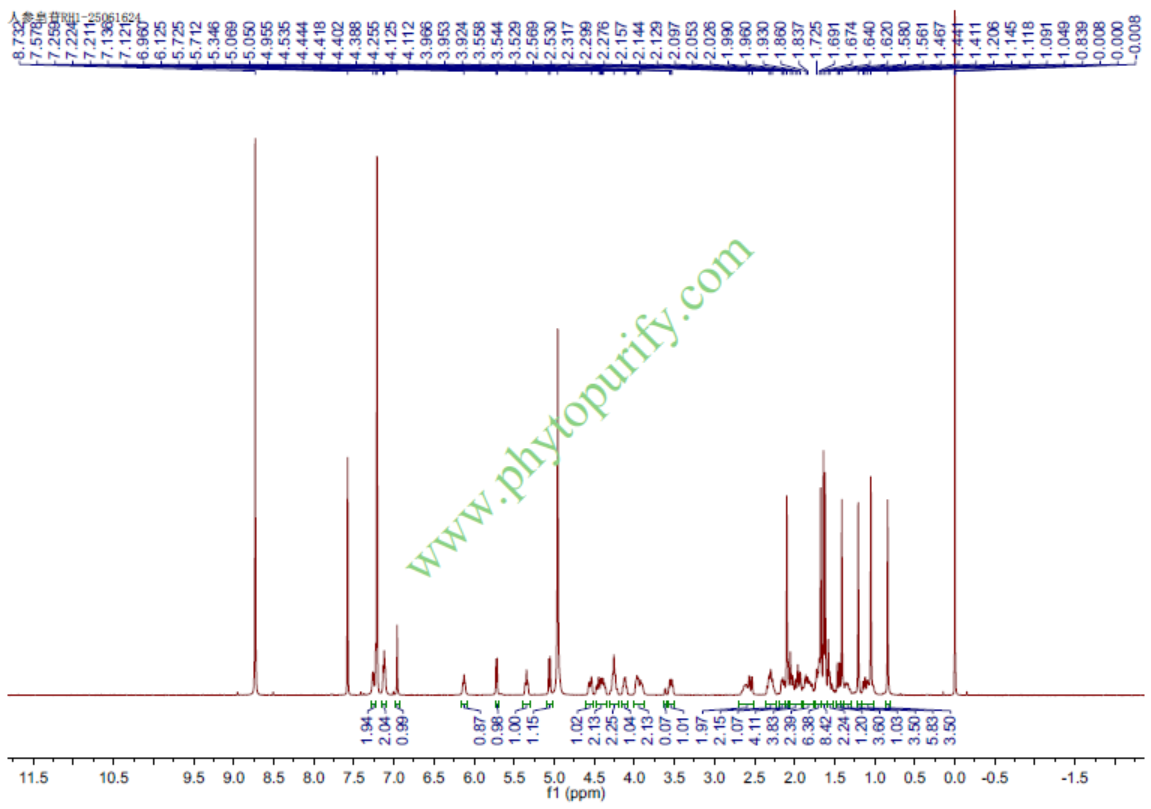
HNMR of Ginsenoside Rh1